Based on Your Reading:
Get Your Free Mesothelioma Guide

Find a Top Mesothelioma Doctor

Access Help Paying for Treatment

Prostate cancer, a disease of the male reproductive system, is the second-most common cancer and the second-leading cause of death among men in the United States.
Written by Suzanne Dixon, MPH, MS, RDN • Edited By Walter Pacheco • Medically Reviewed By Dr. Andrea Wolf
The Mesothelioma Center at Asbestos.com has provided patients and their loved ones the most updated and reliable information on mesothelioma and asbestos exposure since 2006.
Our team of Patient Advocates includes a medical doctor, a registered nurse, health services administrators, veterans, VA-accredited Claims Agents, an oncology patient navigator and hospice care expert. Their combined expertise means we help any mesothelioma patient or loved one through every step of their cancer journey.
More than 30 contributors, including mesothelioma doctors, survivors, health care professionals and other experts, have peer-reviewed our website and written unique research-driven articles to ensure you get the highest-quality medical and health information.
My family has only the highest compliment for the assistance and support that we received from The Mesothelioma Center. This is a staff of compassionate and knowledgeable individuals who respect what your family is experiencing and who go the extra mile to make an unfortunate diagnosis less stressful. Information and assistance were provided by The Mesothelioma Center at no cost to our family.LashawnMesothelioma patient’s daughter


Dixon, S. (2024, January 16). Prostate Cancer. Asbestos.com. Retrieved April 18, 2024, from https://www.asbestos.com/cancer/prostate/
Dixon, Suzanne. "Prostate Cancer." Asbestos.com, 16 Jan 2024, https://www.asbestos.com/cancer/prostate/.
Dixon, Suzanne. "Prostate Cancer." Asbestos.com. Last modified January 16, 2024. https://www.asbestos.com/cancer/prostate/.
Prostate cancer is a disease that occurs when cells in the prostate gland (only found in men) grow abnormally. Approximately 268,490 cases of prostate cancer were diagnosed in the U.S. in 2022.
Men older than 50 are at the highest risk. The 5-year survival rate of prostate cancer is 98% and multiple treatment options are available.
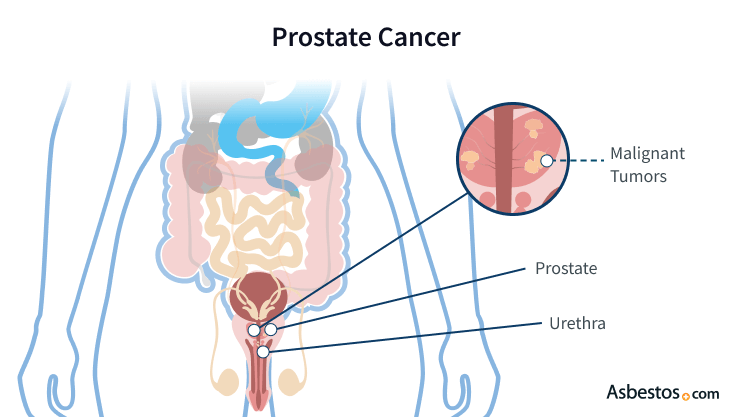
Although specific causes are not completely understood, doctors believe risk factors include age, ethnicity, family history and diet. Asbestos exposure is another potential risk factor under study.
Multiple studies have shown a potential link between asbestos exposure and prostate cancer. A report in February 2020, for example, concluded there was sufficient evidence to suggest asbestos exposure increases prostate cancer risk.
Environmental and occupational exposure correlated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. The main method of absorption was inhalation.
A 2003 study analyzed participants of the Finnish Asbestos Screening Campaign. The study followed the health of 23,285 men and 930 women who worked with asbestos.
These individuals were studied for eight years for cancer occurrence. Results indicated a much higher incidence of prostate cancer when compared to the total Finnish population. Participants were also at a significantly higher risk to develop mesothelioma and lung cancer.

Researchers of a Danish study in 1993 that tested workers at an asbestos cement factory found a 36% increase in the observed number of prostate cancers. The American College of Chest Physicians released a similar study in 1980 that looked at various organs and discovered about half contained asbestos. Of 14 prostate samples, six contained asbestos.
Get Your Free Mesothelioma Guide

Find a Top Mesothelioma Doctor

Access Help Paying for Treatment

There are multiple treatment options for patients diagnosed with prostate cancer. The five most common treatments for prostate cancer include:
When considering the best treatment option for you, discuss your overall health, the stage of your cancer and side effects of treatment with your doctor. You may want to explore your eligibility for available clinical trials with your doctor as well.
Your web browser is no longer supported by Microsoft. Update your browser for more security, speed and compatibility.
If you are looking for mesothelioma support, please contact our Patient Advocates at (855) 404-4592
