Based on Your Reading:
Get Your Free Mesothelioma Guide

Find a Top Mesothelioma Doctor

Access Help Paying for Treatment

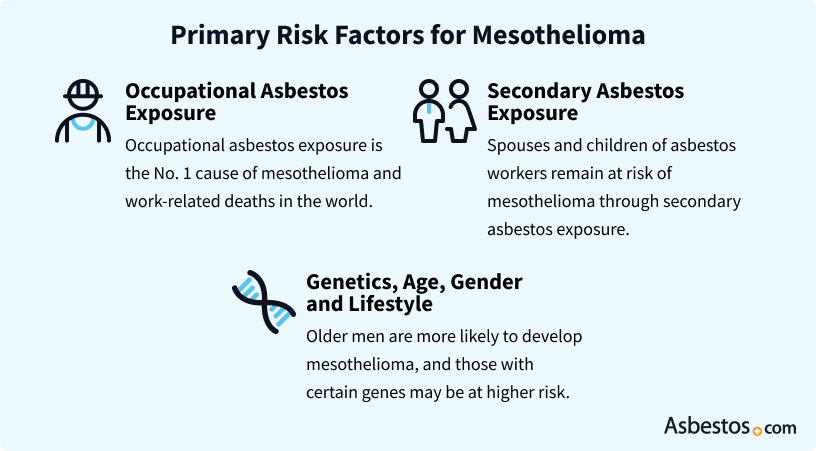
The primary risk factor for mesothelioma is asbestos exposure, including work-related asbestos exposure, secondary asbestos exposure and environmental exposure. Like other cancers, genetic and environmental factors can also increase mesothelioma risk.
Written by Dr. Kristopher Bunting • Edited By Walter Pacheco • Medically Reviewed By Dr. Jacques Fontaine
The Mesothelioma Center at Asbestos.com has provided patients and their loved ones the most updated and reliable information on mesothelioma and asbestos exposure since 2006.
Our team of Patient Advocates includes a medical doctor, a registered nurse, health services administrators, veterans, VA-accredited Claims Agents, an oncology patient navigator and hospice care expert. Their combined expertise means we help any mesothelioma patient or loved one through every step of their cancer journey.
More than 30 contributors, including mesothelioma doctors, survivors, health care professionals and other experts, have peer-reviewed our website and written unique research-driven articles to ensure you get the highest-quality medical and health information.
My family has only the highest compliment for the assistance and support that we received from The Mesothelioma Center. This is a staff of compassionate and knowledgeable individuals who respect what your family is experiencing and who go the extra mile to make an unfortunate diagnosis less stressful. Information and assistance were provided by The Mesothelioma Center at no cost to our family.LashawnMesothelioma patient’s daughter


Bunting, K. (2024, March 7). Mesothelioma Risk Factors. Asbestos.com. Retrieved April 18, 2024, from https://www.asbestos.com/mesothelioma/causes/risk-factors/
Bunting, Kristopher. "Mesothelioma Risk Factors." Asbestos.com, 7 Mar 2024, https://www.asbestos.com/mesothelioma/causes/risk-factors/.
Bunting, Kristopher. "Mesothelioma Risk Factors." Asbestos.com. Last modified March 7, 2024. https://www.asbestos.com/mesothelioma/causes/risk-factors/.
Risk factors are characteristics that increase your likelihood of developing a particular disease. Many risk factors are associated with an increased chance of developing a variety of diseases.
Malignant mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive type of cancer that can affect the lungs, abdomen, heart and testes. Asbestos causes mesothelioma. However, not everyone who is exposed to asbestos will develop mesothelioma, and some cases of mesothelioma are due to other causes. Mesothelioma usually develops 20 to 60 years after asbestos exposure; this means that many people are at risk despite the limited use of asbestos today.
Asbestos exposure is the primary risk factor for mesothelioma. Other risk factors include genetic factors, age, gender and other exposures. Some risk factors can be changed, while others cannot. You can decrease your risk of mesothelioma by reducing your asbestos exposure and other environmental exposures. If you have already been exposed to asbestos, your risk of developing mesothelioma increases as you age, but there are other risk factors that you have some control over.
Asbestos is a naturally occurring fiber found in six different minerals. It has been used as fireproofing and insulation in a variety of industries and consumer products. At one time, asbestos could be found in everything from oven mitts to ceiling tiles. In industry, it was used in many applications where heat resistance or insulation was needed. Asbestos is mined and can be found inside deposits of other minerals, such as vermiculite and talc.
The thin asbestos fibers are most dangerous when they are inhaled, but ingestion and skin contact can also cause asbestos exposure. Asbestos fibers can become airborne due to renovating buildings with asbestos insulation, disturbing asbestos during mining and working with asbestos-containing products.
Any asbestos exposure increases your risk of mesothelioma, but chronic or repeated exposure carries the greatest risk. People who have worked in occupations that use asbestos and asbestos-containing materials, such as shipbuilding or asbestos ore processing, tend to have the highest asbestos exposure.
Teachers, military personnel and others who have worked in buildings made with asbestos can also have high exposure levels. Limited or periodic exposure, such as DIY home renovation or being a student in a classroom with asbestos, may have lower levels of exposure. However, it still increases the risk of developing mesothelioma.
Many different industries have a long history of extensive asbestos use. Shipbuilders, steelworkers, construction workers, firefighters, auto mechanics and people who demolish or renovate old buildings can all have a significantly increased risk of mesothelioma due to occupational exposure.
Currently, the use of asbestos and asbestos-containing products is limited in the U.S. However, since it has been used in such a vast array of industrial and commercial products — such as building materials — occupational exposure still occurs. People who work in occupations that come into contact with older products, such as brake pads and gaskets, floor and ceiling tiles, fume hoods, military equipment and firefighting equipment are at risk of asbestos exposure.
Secondhand asbestos exposure can affect the families of people who have occupational exposure. Asbestos fibers can be carried from the work site to the home on clothing, shoes, hair and tools. Currently, the limited use of asbestos lowers the chances of secondary exposure, but the long latency period between exposure and disease means that mesothelioma risk is still high because of past exposure.
Secondhand exposure to asbestos in the home can occur because of family members doing laundry or children hugging a parent. Spouses and children of those with occupational asbestos exposure have an increased risk of mesothelioma stemming from secondhand exposure.
Environmental asbestos exposure can occur during mining and processing ore containing asbestos as well as disturbance of natural asbestos deposits. Locations where asbestos is present in the ground or soil can produce airborne asbestos fibers when they are disturbed by human activity or natural disasters.
Exposure to airborne asbestos can also occur near work sites where asbestos is used or handled. Communities located near plants that manufacture asbestos-containing products can have significant exposure and increased mesothelioma risk.
Men are more likely than women to develop mesothelioma. Men are also more likely to have occupational asbestos exposure, while women are more likely to have secondary exposure. Women are more likely to be exposed to asbestos through contaminated talc used in talcum powder.
The risk of developing mesothelioma increases with age. This is because mesothelioma typically takes 20 to 60 years to develop after exposure. This does not mean that young people do not get mesothelioma from asbestos exposure. Cases of asbestos-related mesothelioma have been seen in teens and young adults in their 20s.
Genetic factors can increase the risk of various types of cancer, including mesothelioma. Your risk of mesothelioma is higher if you have a family history of mesothelioma.
Specific mutations of a gene called BRCA-associated protein 1 (BAP1) are found in mesothelioma cancer cells in most cases of mesothelioma. Mutations are simply variations of the normal DNA sequence that makes up a gene. These mutations can be inherited from a parent or acquired during a person’s lifetime. Mesothelioma is not inherited. But if a person inherits this specific mutation, it will increase their risk of mesothelioma.
Lifestyle choices, such as diet and smoking, affect the risk of many diseases, including other types of cancer. Tobacco smoking, diet and nutrition are not risk factors for malignant mesothelioma.
Smoking is a risk factor for other types of lung cancer; asbestos exposure increases this risk. Diet and nutrition are not risk factors for mesothelioma but can affect the course of the disease.
Simian Virus 40 is a virus linked to several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. SV40 does not usually cause illness in humans and is not known to cause mesothelioma. However, research indicates that a significant number of mesothelioma cases show the presence of SV40 in cancer cells. Ongoing research will determine whether it is actually a risk factor for mesothelioma.
Exposure to ionizing radiation may be a risk factor for mesothelioma. X-rays, gamma rays and other forms of ionizing radiation are known to increase the risk of numerous types of cancer. Research shows that low-dose radiation from normal X-rays, CT scans and occupational exposure is not a risk factor. However, exposure to high doses of radiation — such as certain types of radiation therapy for tumors — is believed to be a risk factor for mesothelioma, based on the most recent research.
Get Your Free Mesothelioma Guide

Find a Top Mesothelioma Doctor

Access Help Paying for Treatment

People who have worked in industries with significant occupational exposure to asbestos are at the highest risk for developing mesothelioma. This includes veterans and military personnel. Veterans account for 30% of new mesothelioma claims.
Workers in industries that use or have used asbestos are at the highest risk of mesothelioma. Mesothelioma is rare in hobbyists and DIYers, but any amount of asbestos exposure increases your risk of mesothelioma.
Reducing asbestos exposure can lower mesothelioma risk. Unfortunately, past exposure to asbestos cannot be changed. But you can take steps to prevent future exposure.
The risk of occupational asbestos exposure can be lowered by testing and monitoring asbestos levels, using personal protective equipment, following decontamination procedures and having proper training in asbestos safety. If you are at risk of asbestos exposure at work, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration has guidelines and resources to help prevent exposure. Workers who report possible asbestos exposure are protected against discrimination and reprisal through federal whistleblower protection laws.
Removing asbestos — such as during home renovations — poses a significant risk of exposure. Homes built before 1980 may be made with asbestos-containing materials. Do not attempt to remove asbestos yourself. Instead, hire an asbestos abatement professional to test for asbestos, assess exposure risk and properly remove asbestos. Also, when working on older equipment or purchasing vintage items or reclaimed materials, check to see if they may contain asbestos.
Early diagnosis and treatment of mesothelioma are essential to improve life expectancy. If you have any known asbestos exposure, you should talk to your doctor about it. The Mesothelioma Center can assist you in finding a mesothelioma specialist who can assess your risk of mesothelioma and other asbestos-related diseases. Our Patient Advocates can help you find a specialist and schedule a screening.
Mesothelioma has many of the same symptoms as a large number of other medical conditions. If you are experiencing symptoms and are concerned about possible mesothelioma, our Patient Advocates can help you get a second opinion.

Mesothelioma is a rare form of cancer. There are about 3,100 new cases per year in the U.S. There were 0.7 new cases per 100,000 people in 2018. Mesothelioma is very rare in people without any known asbestos exposure, but asbestos exposure significantly increases those odds.
The most common symptoms of mesothelioma are fluid around the lungs, shortness of breath, chest pain, chronic cough and unexplained weight loss. Other cancers, lung disease and heart disease can also cause these symptoms. If you are having any of these symptoms, you should seek medical care.
Most people with asbestos exposure will never develop mesothelioma. However, any asbestos exposure can cause mesothelioma. Chronic exposure carries the highest risk, but even a single exposure can lead to mesothelioma.
If you have been exposed to asbestos and are having any symptoms, you should seek medical attention immediately. Mesothelioma can take decades to develop. Even if you are not experiencing symptoms, you should make sure that your doctor knows about your asbestos exposure. Also, learn all you can about asbestos-related diseases. If you know the signs, you can reduce your risk of further exposure.
Your web browser is no longer supported by Microsoft. Update your browser for more security, speed and compatibility.
If you are looking for mesothelioma support, please contact our Patient Advocates at (855) 404-4592
