
Connect with top-rated doctors specializing in mesothelioma treatment, who will personalize treatment options based on your diagnosis.
Find Your DoctorAlimta, the brand name for pemetrexed, is among the most effective chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma. Doctors often combine Alimta with cisplatin and carboplatin to increase its effectiveness, extend survival rates and improve quality of life for mesothelioma patients.
Alimta, the brand name for pemetrexed, is a chemo drug approved to treat mesothelioma and lung cancer. Doctors have prescribed it as part of the standard chemo protocol for mesothelioma for decades.
In September 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Keytruda (pembrolizumab) in combination with Alimta and cisplatin. The FDA first approved Alimta with cisplatin, a platinum-based chemo drug, in 2004.
Key Facts About Alimta
Alimta arrives at cancer centers in a powder that is mixed into a liquid for injection. Eli Lilly held a patent for Alimta blocking generic availability of pemetrexed until 2022. Now generics have become available, including Pemfexy. It arrives at cancer centers already in liquid form.
Alimta can prolong life expectancy with mesothelioma. It also improves quality of life, reducing symptoms like breathing difficulties and pain.
Alimta blocks DNA replication and prevents mesothelioma cells from rapidly dividing. This prevents mesothelioma tumors from growing and kills them.
Because it blocks the production of folate, Alimta is considered an antifolate antimetabolite. This means it disrupts enzymes involved in cell metabolism.
Dr. Jennifer M. Suga at Kaiser Permanente Medical Center tells us Alimta is more effective when combined with other drugs. “Combining pemetrexed with platinum drugs showed more than 20% improvement in treatment response with more growth control and survival time,” says Dr. Suga.
The recommended dosage for Alimta is 500 mg/m2. A nurse administers it through a port or an IV line for 10 minutes. The guidelines recommend 21 days, known as a cycle, between each IV infusion.
Alimta can help slow tumor growth and kill pleural mesothelioma cells. It improves chest pain, shortness of breath and cough. Alimta has been shown to help pleural patients live around 18 months, particularly when combined with other mesothelioma treatments.
Alimta with cisplatin is the most common chemo regimen for first-line pleural treatment. Though some people tolerate carboplatin better than cisplatin. These drugs help most people live around 16 months. A phase 3 trial found adding Keytruda increases median survival to 17.3 months.
Doctors may recommend chemo with immunotherapy or targeted therapy for advanced cases. Early-stage cases may receive chemo in combination with surgery and radiation. A study of Tumor Treating Fields with Alimta and cisplatin showed a median survival of 18.2 months. A targeted drug trial of Avastin (bevacizumab) with Alimta and cisplatin reported 18.8 months of survival. But there’s a greater risk of adverse events with Avastin.
Doctors use Alimta with cisplatin as a systemic therapy, or whole body therapy, for peritoneal mesothelioma. Similar to treatment plans for pleural patients, doctors often pair Alimta with other mesothelioma medications for peritoneal patients.
Doctors have also used Alimta alone for maintenance chemo. It helps inoperable patients live longer and improves cancer symptoms. Alimta helps peritoneal patients live up to 23 months.
A 2023 case report discussed a peritoneal mesothelioma patient who lived more than 5 years on Alimta maintenance therapy. Doctors generally don’t use Alimta for heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy. That’s because it can lead to significant gastrointestinal toxicity.

Connect with top-rated doctors specializing in mesothelioma treatment, who will personalize treatment options based on your diagnosis.
Find Your DoctorAlimta controls tumor growth, helping people with mesothelioma live longer. It’s a key therapy for this disease, alone or with other treatments. Up to 45% of people with mesothelioma respond to Alimta and cisplatin.
Adding Keytruda helps more people respond to treatment and boosts survival. About 18% more people respond with the addition of Keytruda. They live at least a month longer and have a 21% reduction in the risk of death.
How Alimta Benefits People With Mesothelioma
Plural mesothelioma survivor Lyn Johnson credits Alimta and cisplatin for her survival. Five years after receiving the combo, she tells us it was the only treatment her body could tolerate.
“I was offered Alimta and cisplatin. I can’t lie, this is a hard regime. After 4 sessions, I had a scan,” Lyn shares with us. “My oncologist thought he could see, perhaps, a slight reduction. After the next scan, my oncologist couldn’t believe how much it had shrunk!”
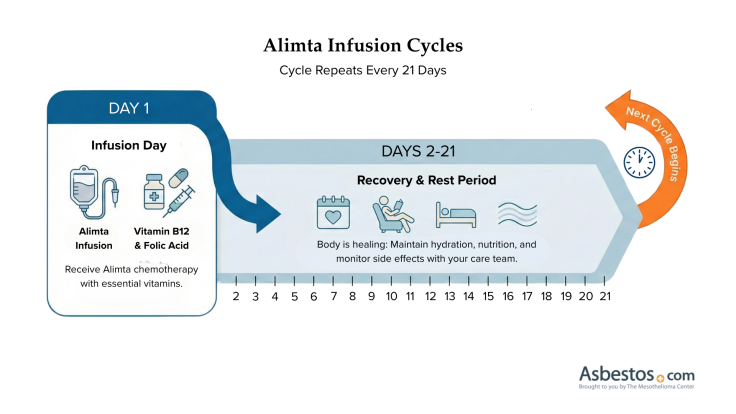
Alimta side effects are usually mild to moderate for most people with mesothelioma. Some people may experience extreme side effects. Inform your doctor of any side effects so they can help you manage them.
Tell your doctor before taking Alimta if you use a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It may cause a drug interaction. NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin and ketoprofen.
Common Alimta Side Effects
People with mesothelioma say taking folic acid and B12 help them tolerate Alimta. For this reason, doctors require these vitamins with pemetrexed therapy.
Those who are pregnant shouldn’t take Alimta because it could harm the unborn baby. If you’re considering Alimta, tell your doctor if you have kidney or liver disease, a weak immune system or excess fluid in your chest cavity.

Kevin Hession
Mesothelioma Survivor Describes His Success With Chemotherapy
Kevin Hession says he actually gained weight following his chemotherapy treatments. “I’ve never had a bad experience with chemotherapy,” Kevin said. “My worst case on a scale of 1 to 10 has probably been a 3.” His treatments have gone so well he was offered an option to take what he calls a “chemo holiday.”
Kevin Hession
Eligibility for pemetrexed treatment depends on your diagnosis and overall health. Doctors assess if someone has co-existing conditions or takes medications that can negatively interact with Alimta as well.
Eligibility Criteria for Pemetrexed
An oncologist’s evaluation confirms eligibility. Ongoing monitoring helps ensure the treatment is safe and effective during therapy.
Clinical trials for mesothelioma continue to explore more effective drug combinations with Alimta. Pemetrexed serves as the baseline chemotherapy drug in these trials.
Current Clinical Trials On Alimta
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends certain drug combinations with pemetrexed. As of 2025, these include cisplatin or carboplatin with or without Keytruda or Avastin.
If you have mesothelioma, talk to your oncologist about Alimta. It’s among the most prescribed treatments for all stages of mesothelioma. You may not qualify if you have severe kidney disease or low blood cell counts.
The FDA approved pemetrexed as a first-line and maintenance therapy for lung cancer. Doctors prescribe Alimta for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. A 2017 study used it with carboplatin followed by maintenance with Alimta alone. The median survival was around 22.6 months.
Before starting Alimta, ask your doctor about its benefits, side effects and how it fits into your treatment plan. Ask about pre-treatment supplements like folic acid and vitamin B12. Also inquire about necessary precautions, how to manage side effects and expected outcomes. Ask if Alimta interacts with your medications or health conditions.
Alimta is expensive, often costing several thousand dollars per treatment without insurance. The total price depends on how many cycles you need. Many insurance plans cover Alimta for mesothelioma and lung cancer.
Pemfexy might be more affordable, but the price may vary throughout the country. People should consult their insurer about co-pays and prior approval. A Patient Advocate can also help answer questions about insurance and financial assistance options.
When combined with other treatments, Alimta helps people with mesothelioma live from 18 to 23 months. Response rates range between 45% and 63% depending on the combination.
Stay up-to-date on treatment, research, clinical trials, doctors and survivors
The information on this website is proprietary and protected. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Any unauthorized or illegal use, copying or dissemination will be prosecuted. Please read our privacy policy and terms of service for more information about our website.
This website and its content may be deemed attorney advertising. Prior results do not predict a similar outcome.
The Mesothelioma Center’s claim as the most trusted resource is based on our more than 150 5-star Google and BBB reviews. Our organization also helps more than half of all mesothelioma patients annually diagnosed.
Your web browser is no longer supported by Microsoft. Update your browser for more security, speed and compatibility.
If you are looking for mesothelioma support, please contact our Patient Advocates at (855) 404-4592
The Mesothelioma Center at Asbestos.com has provided patients and their loved ones the most updated and reliable information on mesothelioma and asbestos exposure since 2006.
Our team of Patient Advocates includes a medical doctor, a registered nurse, health services administrators, veterans, VA-accredited Claims Agents, an oncology patient navigator and hospice care expert. Their combined expertise means we help any mesothelioma patient or loved one through every step of their cancer journey.
More than 30 contributors, including mesothelioma doctors, survivors, health care professionals and other experts, have peer-reviewed our website and written unique research-driven articles to ensure you get the highest-quality medical and health information.
My family has only the highest compliment for the assistance and support that we received from The Mesothelioma Center. This is a staff of compassionate and knowledgeable individuals who respect what your family is experiencing and who go the extra mile to make an unfortunate diagnosis less stressful. Information and assistance were provided by The Mesothelioma Center at no cost to our family.LashawnMesothelioma patient’s daughter


Asbestos.com. (2026, March 9). Alimta. Retrieved March 12, 2026, from https://www.asbestos.com/treatment/chemotherapy/alimta/
"Alimta." Asbestos.com, 9 Mar 2026, https://www.asbestos.com/treatment/chemotherapy/alimta/.
Asbestos.com. "Alimta." Last modified March 9, 2026. https://www.asbestos.com/treatment/chemotherapy/alimta/.

Dr. Arkadiusz Z. Dudek is a medical oncologist at Regions Hospital Cancer Care Center in Minnesota treating several cancers, including pleural mesothelioma.
Our fact-checking process begins with a thorough review of all sources to ensure they are high quality. Then we cross-check the facts with original medical or scientific reports published by those sources, or we validate the facts with reputable news organizations, medical and scientific experts and other health experts. Each page includes all sources for full transparency.
Please read our editorial guidelines to learn more about our content creation and review process.
