Pleural Mesothelioma
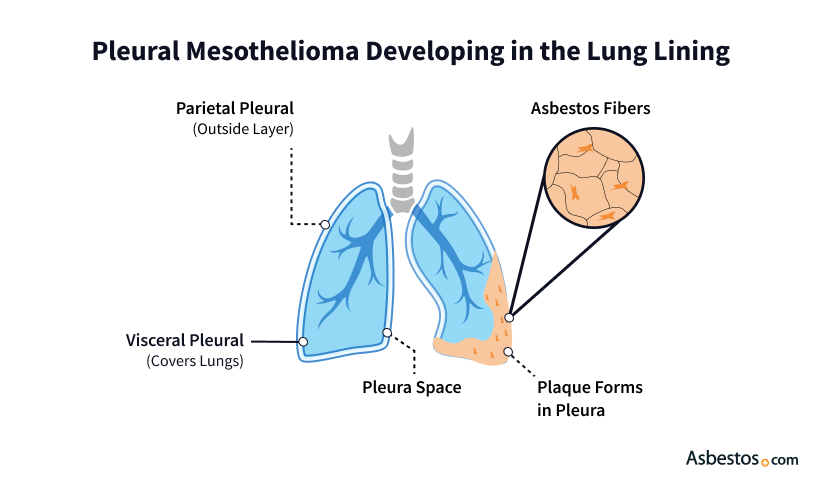
Pleural mesothelioma is a cancer that develops in the protective lining around the lungs (the pleura). Inhaled asbestos fibers can stick to the lining. This may lead to chronic inflammation and tumors. Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath and fluid buildup in the chest.
What Is Pleural Mesothelioma?
Pleural mesothelioma is a cancer that develops in the thin membrane that covers your lungs and lines your chest cavity. This membrane is called the pleura. At first, tumors typically look like plaques or nodules. They can sometimes look like other cancers, making accurately identifying them challenging. As pleural mesothelioma progresses, tumors can merge to form a sheet-like mass.
Your pleura, also known as the pleural membrane, protects your lungs. It helps your lungs move smoothly when you’re breathing. Pleural mesothelioma can affect how your pleura works, causing it to thicken or build up fluid. This can make breathing difficult and painful.
Key Facts About Pleural Mesothelioma
- Inhaling asbestos fibers is the main cause of pleural mesothelioma.
- It starts in the pleura, the thin membrane that lines the lungs and chest wall.
- Chest pain, shortness of breath and persistent cough are common symptoms. Pleural effusion, or fluid buildup around the lungs, can be one of the first signs.
- It can take 20 to 60 years after asbestos exposure for symptoms to develop.
- Treatments may include immunotherapy, chemotherapy, surgery and radiation.
Doctors diagnosed about 2,100 new pleural mesothelioma cases in the U.S. in 2021, the year of the latest available data. But it’s the most common type of mesothelioma, making up about 75% of all cases. This cancer is almost always linked to asbestos. The toxic mineral was used a lot in construction, manufacturing and other industries.
Since pleural mesothelioma is rare, patients may not have heard of it until they receive a diagnosis. “We had no idea what it was,” Jeanne Niemiec tells us. Her husband, Bob, received a pleural mesothelioma diagnosis in 2019. “I’d never even heard of it before, and neither had Bob or our kids.”
What Causes Pleural Mesothelioma?
The main cause of pleural mesothelioma is asbestos exposure. When asbestos fibers are inhaled they can get stuck in the pleura, irritating it and causing scar tissue to form over time.
Over many decades, this irritation from asbestos fibers can change cell DNA. These DNA mutations can lead to cancer. Some researchers say other factors may play a role. Radiation and genetic mutations, such as BAP1 mutations, can also contribute to the development of mesothelioma. But asbestos exposure remains the main cause.
Risk Factors for Pleural Mesothelioma
Occupational asbestos exposure is the No. 1 cause of pleural mesothelioma. Many jobs put workers at risk of asbestos exposure. Construction, manufacturing, the military and shipbuilding, for example, all heavily used asbestos. While most companies phased out asbestos in the 1980s and 1990s, today workers may come into contact with older or legacy asbestos products.
Who Is at Risk of Asbestos Exposure?
- Auto mechanics
- Construction workers
- Demolition crews
- Factory and industrial workers
- Firefighters
- Insulators
- Military personnel
- Miners
- Power plant workers
- Shipyard workers
People living with those who come into contact with asbestos at work can also be at risk of developing pleural mesothelioma. Asbestos fibers can be brought home on clothing, shoes, gear, skin and hair. This is called secondary asbestos exposure.
Secondary exposure led to Shaun Bigbie’s pleural mesothelioma diagnosis. His father and uncle encountered asbestos while working at the Ford Motor Company. Shaun tells us, “They think somewhere along the line my father brought asbestos on his clothing home to me. My uncle said there were days you would just see fibers everywhere in the air.”

Understand your diagnosis, top doctors and ways to afford care.
Get Your Free GuideWhat Are the Symptoms of Pleural Mesothelioma?
The most common symptoms of pleural mesothelioma are shortness of breath, back and chest pain and fatigue. Fluid around your lungs, called pleural effusions, can be one of the first signs of this disease. Pleural thickening and pleural plaques can also be signs.
Doctors diagnosed Joey Barna with pleural mesothelioma after he felt fluid in his lungs. His symptoms were first mistaken for pneumonia. Our Patient Advocates helped him get a proper diagnosis and treatment. Despite having a rough time at first, he tells us he’s feeling great today and is living life to the fullest.
Common Pleural Mesothelioma Symptoms
Early signs of pleural mesothelioma can feel mild and easy to ignore. Some people wait to see a doctor until the cancer gets worse. It’s important to talk to your doctor if you feel sick or something doesn’t feel right. Finding mesothelioma early can help you get better care.
If you have a history of asbestos exposure, it’s important to note your risk when discussing your symptoms with your doctor. This can help confirm a diagnosis as early as possible.
How Is Pleural Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
A pleural mesothelioma diagnosis typically begins with a physical exam and imaging scans like chest X-rays and CT scans. If your scans show fluid buildup or pleural thickening, your doctor will order a biopsy to analyze a tissue sample. A biopsy is necessary to confirm a pleural mesothelioma diagnosis.
Tests Used to Diagnose Pleural Mesothelioma
- Physical Exam: First your doctor will check for abnormalities, like a skin bump. They’ll also check tender or painful areas.
- Blood Tests: Next, blood may be drawn. These tests allow experts to look for signs like biomarkers, such as proteins or certain genetic mutations, that can indicate pleural mesothelioma.
- Imaging Scans: X-rays, MRI, CT and PET scans help spot the location of pleural tumors.
- Biopsy: During a short surgery, your doctor will remove a small piece of tissue to check for pleural cancer cells.
Getting a second opinion from a pleural mesothelioma expert can help make sure your diagnosis is correct. This rare cancer is sometimes mistaken for other illnesses. Seeing a specialist can help you get the right care. It’s OK to ask for another doctor’s opinion.

Exclusive Content
Jeanette Mednicoff: Advice for someone who has a loved one diagnosed with mesothelioma
Support does come in many different forms and different manners.
I think that emotional support, first and foremost, is huge just being there for them just listening to them, just letting them, you know, lean on you to tell you whatever it is they’re feeling. Because they’re probably gonna have some really big feelings about what’s going on. Support can also be showing up with meals, you know, helping with errands, going over and, you know. Perhaps offering to clean the house, just sit and have a cup of tea. Kim loves, to drink tea. Just being there for her, just really showing up however you can.
Ask them, you know, “what can I do to help you?”
I think one of the things I discovered is that I kinda had a catchphrase with Kim. So quite often through this whole entire journey from start to finish or to where we are here today.
One thing I would do is call her on the phone and say, what do you need from me?
Basically, what can I do to help you?
Is it making calls? Is it, you know, scheduling something? Whatever it is, I would say that’s the best way to support your friend or family member with this diagnosis.
Stages of Pleural Mesothelioma
Your pathology report will likely tell you the stage of your pleural mesothelioma. Stages show how far your cancer has progressed. Early mesothelioma stages mean tumors are close to the area where they first developed. Later stages mean cancer has spread further.
Pleural Mesothelioma Stages
- Stage 1: Tumors form in and around the pleura of one lung.
- Stage 2: Cancer cells spread beyond the pleura, entering nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: Cancer spreads to tissues in the chest and distant lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: Distant parts of the body, like the liver and bones, are affected.
Doctors use what’s called the TNM staging system for pleural mesothelioma. TNM stands for tumor, node and metastasis. This refers to the cancerous growths, if they’ve spread to lymph nodes and if they’ve spread even further in your body.
Dr. Jeffrey Velotta, a pleural mesothelioma expert at Kaiser Permanente Oakland Medical Center, talked to us about new updates to the TNM for pleural mesothelioma. The American Joint Committee on Cancer included more details to refine the staging process in January 2025. Dr. Velotta explains, “Standardizing measurements of tumors can help improve treatment guidelines and prognostic information.”
Treatment Options for Pleural Mesothelioma
Doctors treat pleural mesothelioma with surgery, medicine and other therapies. Sometimes, they combine more than one kind of treatment to help you feel better or live longer. Doctors call this multimodal therapy. Other care, like pain relief, also helps improve daily life.
- Chemotherapy: These drugs kill pleural cancer cells or slow their growth. Common ones include Alimta (pemetrexed), Paraplatin (carboplatin) and Platinol (cisplatin).
- Clinical trials: Doctors test new treatments in clinical trials. You may qualify to try new therapies for pleural mesothelioma.
- Immunotherapy: This helps your body’s immune system fight cancer. It even helps resistant cell types of pleural mesothelioma. Common drugs include Keytruda (pembrolizumab), Opdivo (nivolumab) and Yervoy (ipilimumab).
- Palliative care: This care focuses on helping you feel better, not curing cancer. It can be used to manage both disease symptoms and treatment side effects like using medicine to ease pain.
- Radiation therapy: This uses strong X-rays to kill pleural mesothelioma cells or shrink tumors. It can help with treatment or make you feel more comfortable.
- Surgery: Doctors may remove the tumor, the lung or the lining of the lung to help treat the cancer. This is usually done in the early stages and may be used with other treatments.
In January 2025, cancer experts shared new guidelines for treating pleural mesothelioma. They now suggest using treatments that keep the lung instead of removing it. Immunotherapy is often preferred over chemo because it may help people live longer. A new drug mix, including Keytruda and chemo, was also approved to treat advanced cases.
Treatment Recommendations Among Doctors
The Mesothelioma Center surveyed doctors and nurses in 2025 about the best treatment approaches for people with pleural mesothelioma. Respondents said the main approach is chemotherapy with immunotherapy, which aligns with the newest treatment options for pleural mesothelioma.
| Treatment Approach | % of Respondents |
|---|---|
| Chemotherapy + Immunotherapy | 39% |
| Surgery (e.g., P/D or extrapleural pneumonectomy) | 18% |
| Multimodal (combination of surgery, chemo, immunotherapy, radiation) | 17% |
| Chemotherapy (e.g., pemetrexed + cisplatin/carboplatin) | 16% |
| Palliative/supportive care | 10% |
Finding the Best Pleural Mesothelioma Doctor
Pleural mesothelioma specialists include oncologists, surgeons and radiologists. They work at mesothelioma treatment centers across the country. Finding the right specialist for you can depend on the stage of your cancer. Your treatment goals and preferences matter, too.
Your doctor can help refer you to a specialist. Patient Advocates can also help match you with a specialist. They’ll find one who has a lot of experience treating similar cases as yours.
“With this disease, finding a specialist is critical,” Dr. Jacques Fontaine shares with us. He heads the Mesothelioma Research and Treatment Center at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa. “You need someone who truly understands it. They must know how to treat it aggressively for the best outcome.”
Filled with thoughtful items to bring comfort and encouragement while undergoing treatment.
Get Your Free KitPrognosis for Pleural Mesothelioma
Pleural mesothelioma prognosis is usually poor, but outcomes are individual, and some factors can improve it. These numbers are estimates. They don’t predict exactly what will happen to you. Everyone is different, and your doctor can help explain what these numbers mean for you.
| Pleural Mesothelioma Stage | Average Life Expectancy | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Stage I | 21 months or more | 22.5% |
| Stage II | 19 months to 5 years | 11% |
| Stage III | 16 months to 4.5 years | 16% |
| Stage IV | 12 months to 2 years | 7% |
Life expectancy is the average amount of time a person may live with pleural mesothelioma. The survival rate shows how many people are still alive after a certain amount of time. Life expectancy is often less than 18 months. The median survival ranges from 8 to 14 months. An early-stage diagnosis at a younger age helps. So does aggressive treatment and good overall health.
Factors That Affect Prognosis
Predicting someone’s prognosis is complex and challenging. A number of factors play a role. Some survivors have lived with pleural mesothelioma for many years.
- Age: Younger patients tend to live longer.
- Cell type: Your specific mesothelioma cell type can impact how effective treatment is.
- Gender: Women tend to live longer with the disease than men.
- Healthy lifestyle: Those who exercise and have better nutrition tend to have a better prognosis.
- Pleural fluid: Those with more pleural fluid in their chest often have a worse prognosis.
- Recurrence: Mesothelioma returning is associated with a poorer prognosis.
- Stage: This is the most important factor. A diagnosis in the early stages may lengthen survival.
No doctor can determine your life expectancy based only on a diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma. This cancer advances at a rapid pace, but treatment can control it. Treatment advances are helping people live longer and enjoy a better quality of life.
Living With Pleural Mesothelioma
Long-time survivor Michael Cole shares his tips for living with pleural mesothelioma. He recommends staying hydrated, eating a healthy diet and staying active. He also says, “It is crucial to maintain good mental health.”
5 Tips for Living With Pleural Mesothelioma
- Eat healthy foods like fruits and vegetables to help your body stay strong.
- Find ways to relax, like deep breathing or listening to music, to feel less stressed.
- Stay connected with people who care about you, like family and friends, for support.
- Talk to your doctor about any pain you have and how to manage it.
- Try to move your body every day, even if it’s just a short walk.
Sissy Hoffman has lived with pleural mesothelioma for nearly 30 years since her diagnosis in 1996. She credits Dr. David Sugarbaker for her success. “Dr. Sugarbaker not only extended my life, but he forced me to live a fuller life,” Hoffman tells us. She has returned to teaching, travelling and volunteering.
- A 2024 UC San Diego Health clinical review emphasized the importance of learning more about molecular characteristics of pleural mesothelioma to better diagnose and treat it.
- Pleural mesothelioma specialists tap into the advancements in treating this disease to improve patients’ survival rates.
“With pleural mesothelioma, it’s critical to find a specialist who has knowledge of the disease and the treatment and expertise in this field. Finding the right specialist and a Center of Excellence will give patients access to the full array of treatment options and options for clinical trials, which will provide more treatment options.”
Questions Our Patients Advocates Are Commonly Asked
We asked our team of Patient Advocates here at The Mesothelioma Center what pleural patients ask when they call us. They’ve shared these questions along with their helpful answers.
- Is there a cure for pleural mesothelioma?
-
There is no sure cure for pleural mesothelioma, but treatment can help people live longer and feel better. Doctors can use medicine, surgery or other methods to slow the cancer. If the cancer is found early and removed with surgery, some people can live for years. Care teams work to give the best help possible.
- Do I need a second opinion about my diagnosis?
-
Getting a second opinion from a pleural mesothelioma expert can help make sure your diagnosis is right. This rare cancer is sometimes misdiagnosed. If you were around asbestos, it’s important to talk to a doctor who knows about this disease. We can help connect you with experts and make the process easier.
- How do I know which treatment option is best for me?
-
If you’re not sure about your treatment choices, talking to a specialist can help. Different doctors may suggest different options, and it’s OK to ask questions. Some people choose aggressive surgery that may be hard but could help them live longer. Others may decide not to get treatment at all—it’s a personal choice.
- Can my pleural mesothelioma be passed on to my children or grandchildren?
-
Some families have more than one person get sick with asbestos-related diseases. This can happen when family members are exposed at work, at home or in the environment. Some people may also have higher risks because of their genes. Talk to your doctor about your risk and if you should get checked regularly.





