Christine S. was diagnosed with epithelial mesothelioma after nearly a year of unanswered questions and pleurisy and pneumonia misdiagnoses. She remained resilient through 6 intense rounds of chemo. Today, she shares her experience to raise awareness about the risks of secondary asbestos exposure and advocate for earlier diagnosis of mesothelioma.
Epithelioid Mesothelioma
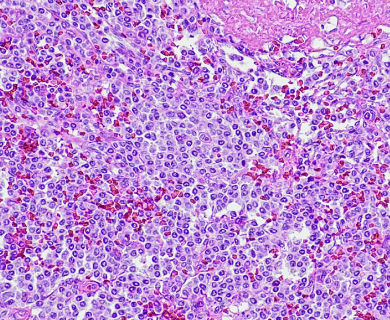
Epithelioid mesothelioma is a subtype of a rare and malignant asbestos-related cancer. Its name refers to a type of specific cell in mesothelioma tumors. Epithelioid cells respond better to treatment than other mesothelioma cell types. This subtype accounts for 50% to 70% of all mesothelioma cases.
What Is Epithelial Mesothelioma?
Epithelial mesothelioma is an aggressive form of mesothelioma cancer that develops on the tissue that lines the organs of your body. This membrane, called the mesothelium, is made of cells like epithelial cells. Inhaled asbestos fibers can get stuck in that membrane and cause irritation that changes the DNA of the cells, making them cancerous.
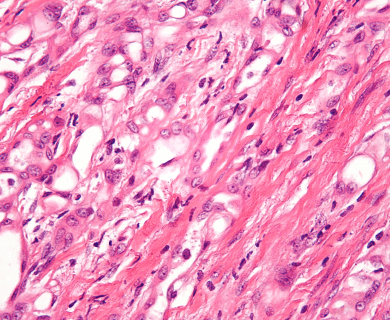
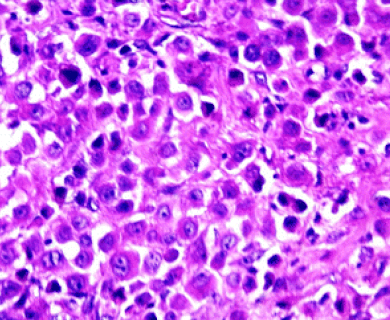
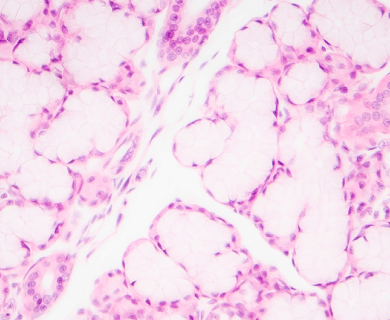
Pathologists look at tumor and tissue samples and determine what cells they can see. If the majority of cells from your mesothelioma sample are epithelioid cells, your mesothelioma subtype is determined to be epithelioid mesothelioma.
Key Characteristics About Epithelioid Mesothelioma
- About 54% of pleural mesothelioma tumors contain epithelial cells.
- Doctors diagnose 1,500 to 2,100 epithelioid mesothelioma patients annually.
- Epithelioid cells comprise about 75% of peritoneal mesothelioma tumors.
- The epithelioid type has the best prognosis of all types of mesothelioma.
“Epithelioid” and “epithelial” are sometimes used in ways that feel interchangeable. But epithelial cells are normal cells that line the skin and the inside of organs. Epithelioid cells can be found in both cancerous and non-cancerous conditions. Epithelioid cells look like epithelial cells, which are shaped like columns or cubes. However, epithelioid cells may come from different types of cells that have mutated or changed shape, taking on an appearance similar to epithelial cells.
The epithelioid subtype of mesothelioma has a more favorable prognosis. Epithelioid cells respond better to aggressive treatment than sarcomatoid cells. Having a combination of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells is called biphasic mesothelioma. People with this subtype benefit if they have more epithelioid than sarcomatoid cells.
Epithelioid Mesothelioma Symptoms
Epithelioid mesothelioma symptoms often include cough, shortness of breath and lack of appetite. Symptoms can depend on where on the mesothelium the cancer develops: the lining of the lungs (pleura), abdomen (peritoneum), heart (pericardium) or testes (tunica vaginalis).
Common Symptoms of Epithelioid Mesothelioma
- Abdominal pain or bloating
- Ascites or fluid buildup in the belly (peritoneal effusion)
- Bowel or bladder changes
- Chest tightness or pain
- Cough, hoarseness or difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- Fatigue
- Fever or night sweats
- Fluid buildup in the chest (pleural effusion)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhea
- Shortness of breath
- Unexplained weight loss
Studies show early symptoms may be mild, making it difficult to diagnose. Late diagnosis can cause delays in treatment. As the disease progresses and tumors increase in size and spread, more severe symptoms may appear.
Mesothelioma cancer symptoms are the same, no matter the cell type. But the cell type affects which treatments are most helpful. Talk to your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
Find the top cancer centers trusted by mesothelioma patients nationwide.
Get Help NowWhat Causes Epithelial Mesothelioma?
The primary risk factor and cause of epithelioid mesothelioma is asbestos exposure. This is true for other types of mesothelioma as well. Inhaling or swallowing asbestos fibers causes inflammation and DNA damage. This can lead to cancer many years later.
People are commonly exposed to asbestos at work, in the environment, from contaminated talc or damaged asbestos products in homes, schools or other older buildings. Not everyone exposed to asbestos develops mesothelioma, though there is no safe amount of exposure. Additional risk factors can include the amount and length of exposure and possible genetic predispositions for developing cancer.
Many people with epithelioid mesothelioma worked with asbestos products years before their diagnosis. All mesothelioma cell types have a latency period of 20 to 60 years. The first symptoms may not appear for decades after the initial asbestos exposure.
How Is Epithelioid Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
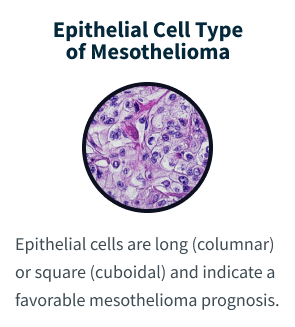
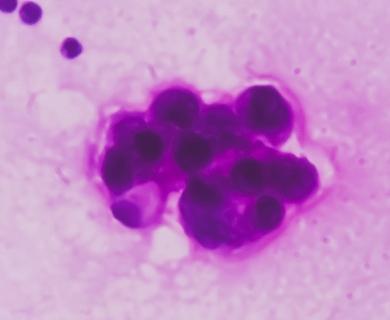
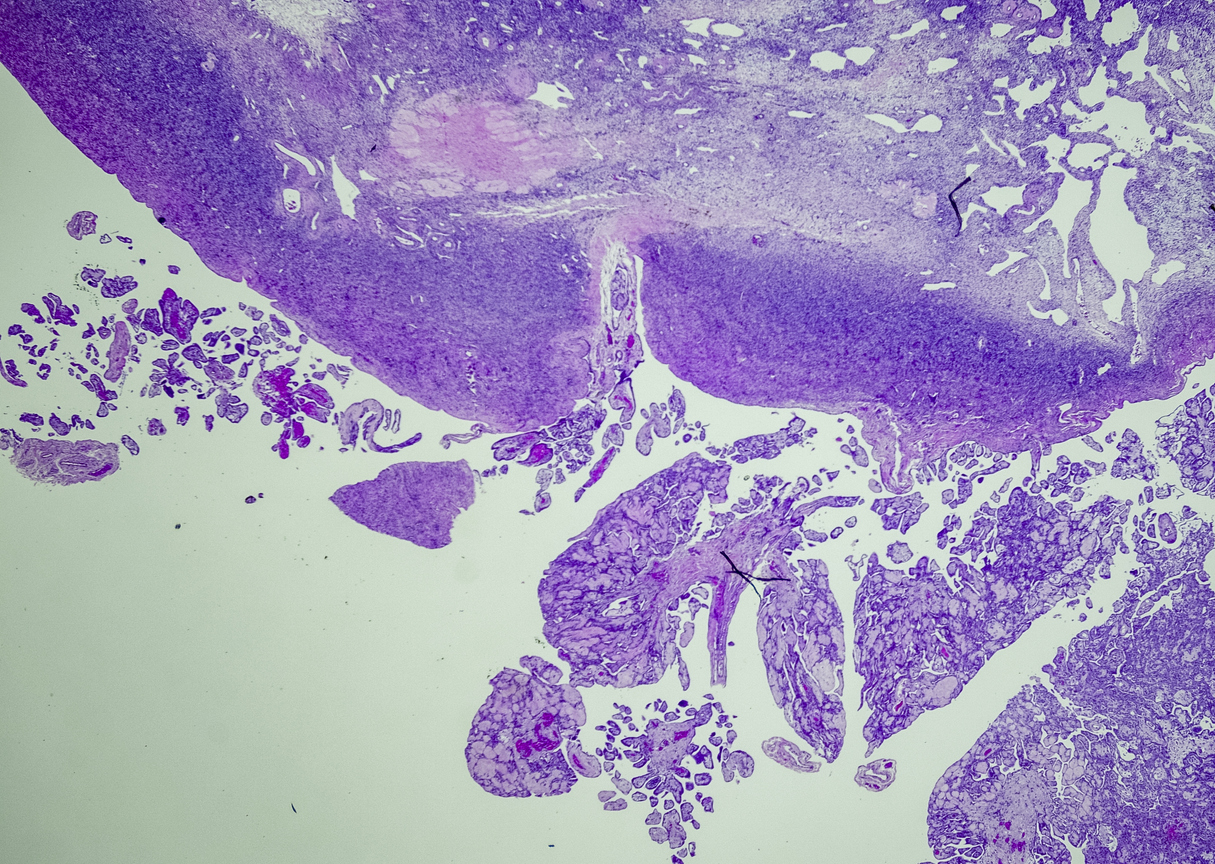
A tissue biopsy is the only way to diagnose epithelioid mesothelioma. This procedure involves taking samples of suspicious tissue. Pathologists examine the tissue samples under a microscope to identify specific cell characteristics.
Epithelioid mesothelioma cells clump together in groups and don’t tend to travel. These cell types are less likely to spread to other areas of the body. When a pathologist confirms the presence of specific cancer cells, an accurate diagnosis of your mesothelioma type can be made.
Your mesothelioma doctor will review your detailed personal pathology report that describes the types of mesothelioma cells found. You and your doctor will discuss the types of treatments that typically work best for epithelioid mesothelioma, your overall health and goals to determine which therapy options may be best for you.
Diagnosing Epithelial Mesothelioma With Immunohistochemistry
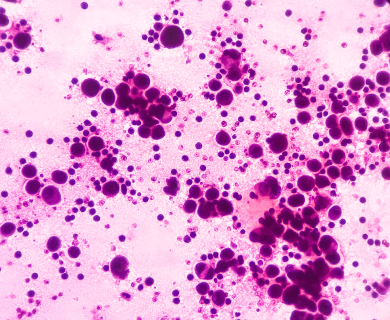
The tool or technique for studying cancer tissues is called immunohistochemistry. Pathologists look at stained samples, testing for certain proteins linked to epithelial cells. If pathologists find proteins from other cancers, they’ll rule out epithelioid mesothelioma.
The proteins that help doctors identify epithelioid mesothelioma from different types of cancer include: calretinin, D2-40, keratin 5/6, podoplanin and WT-1 protein. An official diagnosis depends on more than just immunohistochemistry. It also considers the tumor’s appearance, location and cell traits.
Epithelial subtype mesothelioma describes the type of cells the pathologist is seeing under the microscope when they look at a patient’s tumor.
Subtypes of Epithelial Mesothelioma Cells
While epithelioid is a subtype of mesothelioma, there are further subtypes of the epithelioid type. Pathologists can identify these cell subtypes with immunohistochemistry.
Epithelioid mesothelioma has a better prognosis than other subtypes, but some epithelioid cell subtypes also have better prognoses than others. For example, adenomatoid cells are associated with a better mesothelioma survival rate.
Patient Advocate Danielle DiPietro explains why it’s so important to diagnose your cell subtypes. Daniells tells us, “When I speak with a patient who is hesitant to have a biopsy, which is rare, I explain that diagnosing the cell type is imperative for assessing treatment options.”
How Is Epithelioid Mesothelioma Treated?
Doctors often use a mix of chemotherapy, immunotherapy and surgery to treat epithelioid mesothelioma. A treatment plan for mesothelioma should include 2 or more types of therapy. No single treatment can fully control cancer. Using different therapies together can help patients live longer.
People diagnosed in early stages usually undergo intense treatment. This can involve surgery, chemo and radiation therapy. People with late-stage cancer respond well to palliative care. This includes immunotherapy, chemo and Tumor Treating Fields. However, palliative care can be helpful at any stage.
Common Epithelioid Mesothelioma Treatments
- Chemo: Chemo drugs penetrate and attack mesothelioma cells, either destroying them or preventing their spread. This treatment can triple the mesothelioma survival rate.
- Combination therapy: Mixing treatment approaches, or multimodal therapy, integrates multiple mesothelioma treatments to fight cancer from different angles.
- Immunotherapy: Harnessesing the body’s immune system to fight mesothelioma, immunotherapy can extend survival to 18 months for many patients.
- Radiation: Ionizing radiation, including high-energy X-rays or particles, is used in radiation therapy therapy to destroy cancer cells. This helps shrink tumors, relieve pain and reduce the risk of recurrence and spread.
- Surgery: Procedures like extrapleural pneumonectomy or EPP and pleurectomy with decortication or P/D are common surgeries for pleural mesothelioma. Tumor removing surgery like cytoreduction with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy, known as HIPEC, is used for peritoneal mesothelioma.
“While early stages of mesothelioma tend to have more possibilities for treatment options, not all patients in early-stage mesothelioma will be candidates for every treatment option available,” explains Dr. Catherine Perrault, a board-certified family physician and Medical Officer at The Mesothelioma Center. “Having that discussion with your multidisciplinary team to know why or why you may not be a good candidate for different treatments is important.”
Many people with mesothelioma want a second opinion about their mesothelioma treatment options. Patient Advocates can guide you to experienced mesothelioma specialists at top cancer centers who can give you additional insights or possibly offer other options. Patient Advocates or your health care team can also help you find clinical trials you may qualify for that test cutting-edge new therapies or advancements to existing approaches.

Understand your diagnosis, top doctors and ways to afford care.
Get Your Free GuideEpithelial Mesothelioma Life Expectancy and Prognosis
The average life expectancy for patients with epithelial mesothelioma who have surgery is 18 months. A study from the National Cancer Institute shows the 5-year survival rate for epithelioid pleural mesothelioma is 12%.
Another study on peritoneal mesothelioma found patients with epithelioid cells lived a median of roughly 5 years. In contrast, those with sarcomatoid or biphasic cells had a median survival of only 7 to 13 months.
People with epithelioid mesothelioma live 200 days longer on average than those with other cell types. The overall survival of all cell types declines when the disease metastasizes or spreads.
Epithelioid mesothelioma has a better prognosis than biphasic and sarcomatoid types. Epithelioid cells also respond the best to treatment and don’t spread as quickly as other cell types, leading to longer survival.
The survival rate for epithelial patients is overall significantly longer. Epithelial cell type is the best mesothelioma cell type to have. This patient will have more options, such as surgery, and is more likely to respond to treatment.
Common Questions About Epithelioid Mesothelioma
- Where can I get treatment for epithelial cell mesothelioma?
-
Look for mesothelioma specialists with years of experience treating peritoneal and pleural mesothelioma. Oncologists need training to treat epithelioid mesothelioma. Our Patient Advocates can help you find a top doctor who treats epithelial mesothelioma.
- Is epithelioid mesothelioma curable?
-
Unfortunately, epithelioid mesothelioma has no cure. But patients with the epithelioid cell type have the most treatment options. This cell type responds the best to all forms of treatment.
- Is there any ongoing research on epithelioid mesothelioma?
-
Researchers are constantly looking for mesothelioma patients with the epithelioid cell type for clinical trials. As of March 2025, several clinical trials are recruiting patients. Studying epithelioid patients lets researchers learn how a drug or therapy will affect most patients diagnosed with mesothelioma. A clinical trial completed in 2024 examined the effectiveness of Itraconazole and Rifampin used on epithelioid mesothelioma patients. Final results haven’t been published.