Jim Madaris developed pleural effusion after abdominal surgery with HIPEC for peritoneal mesothelioma because the tumor cells migrated into the thoracic cavity. Doctors first used a thoracentesis to drain the fluid. Eventually, he received a pleurodesis to eliminate the space between the lungs and the chest wall.
Mesothelioma Biopsy
A biopsy is the only sure way to diagnose mesothelioma. A mesothelioma biopsy collects tissue or fluid to check for cancer. Doctors may recommend biopsies for people with symptoms of mesothelioma or a known history of asbestos exposure.
What Is a Mesothelioma Biopsy?
A mesothelioma biopsy is a medical test. Your doctor collects a sample of suspected cancer cells or tissue for lab testing. It’s the most accurate way to confirm mesothelioma, a cancer often mistaken for benign illnesses or other cancers.
Biopsy procedures can take 30 minutes to 3 hours. They may require general anesthesia. Your doctor then sends your biopsied cells to a pathologist. They will look for signs of cancer. Laboratory tests can help determine if you have mesothelioma. These tests show the types of cancer cells present, which help guide treatment for you.
To diagnose mesothelioma, doctors use biopsies, imaging scans and blood tests. The type of biopsy a patient needs depends on the location of the tumor. There are several types of biopsies: an endoscopic biopsy, a fine-needle biopsy and a surgical biopsy. Doctors tailor each type of biopsy to access different body parts. This helps provide accurate diagnoses.
Key Facts About Mesothelioma Biopsies
- Doctors need a biopsy for an accurate mesothelioma diagnosis.
- Biopsies can sample tumors and lymph nodes for cancer cells.
- Biopsies can help find out if cancer has spread.
- Pleural mesothelioma requires a biopsy using video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery.
- Peritoneal mesothelioma requires a core needle biopsy or laparoscopic biopsy.
Endoscopic Mesothelioma Biopsies
Endoscopic biopsies are minimally invasive procedures used to diagnose mesothelioma. These procedures need general anesthesia. They usually require an overnight hospital stay, especially if the chest is involved.
To perform an endoscopic biopsy, your doctor will insert an endoscope. It’s a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and camera. The doctor will use a small incision to insert the device. An endoscope will help your doctor find cancer cells and collect a tissue sample for testing.
Back in 2005, I started developing pain in my abdomen. In June, it was decided that I would have a laparoscopic surgery to check my appendix and determine if I had endometriosis. They removed three tumors from the lining of my abdomen to be biopsied. I had been diagnosed with well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma of the peritoneum.
Recovery from general anesthesia can take hours. The patient may feel groggy, confused and in pain. A short hospital stay ensures the patient recovers before going home. Doctors may also prescribe antibiotics for up to a week.
Types of Endoscopic Biopsies for Mesothelioma
There are several types of endoscopic biopsies. Doctors often choose endoscopic biopsies because they can collect large samples of tumors.
- Laparoscopy: During a laparoscopy, a surgeon makes an abdominal incision and inserts an endoscope. Surgeons may also need to make small cuts to insert surgical tools. This procedure can diagnose peritoneal mesothelioma. Doctors examine the abdominal cavity and collect samples of tissue and fluid.
- Mediastinoscopy: This procedure can help diagnose pleural mesothelioma and stage it. A surgeon may perform a mediastinoscopy while the anesthetized patient undergoes a thoracoscopy. A surgeon inserts an endoscope at the neck’s base to sample the lymph nodes around the windpipe.
- Thoracoscopy and Video-Assisted Thoracoscopy: During a thoracoscopy, a surgeon inserts an endoscope between the ribs. It can remove excess fluid, examines the chest and takes tissue samples. VATS is a more complex type of thoracoscopy. A surgeon inserts an endoscope and tools into the chest through small incisions. VATS can collect large samples from multiple sites in the chest.
Endoscopic biopsies can lead to bleeding and infection. After the procedure, the doctor may limit some activities. Some patients may have stitches that need removal in 1 to 2 weeks.

Understand your diagnosis, top doctors and ways to afford care.
Get Your Free GuideFine-Needle Biopsy for Mesothelioma
A fine-needle biopsy for mesothelioma is a quicker, less invasive test than endoscopy. It’s not as effective as thoracoscopy for diagnosing pleural mesothelioma. But, it can be a safer alternative for some patients. It’s also effective in diagnosing peritoneal mesothelioma.
It is usually done as an outpatient procedure with local anesthesia. It uses a long, hollow needle attached to a syringe to remove up to 10,000 sample cells for analysis. Your doctor will usually use an ultrasound or CT scan to guide the needle to the target.
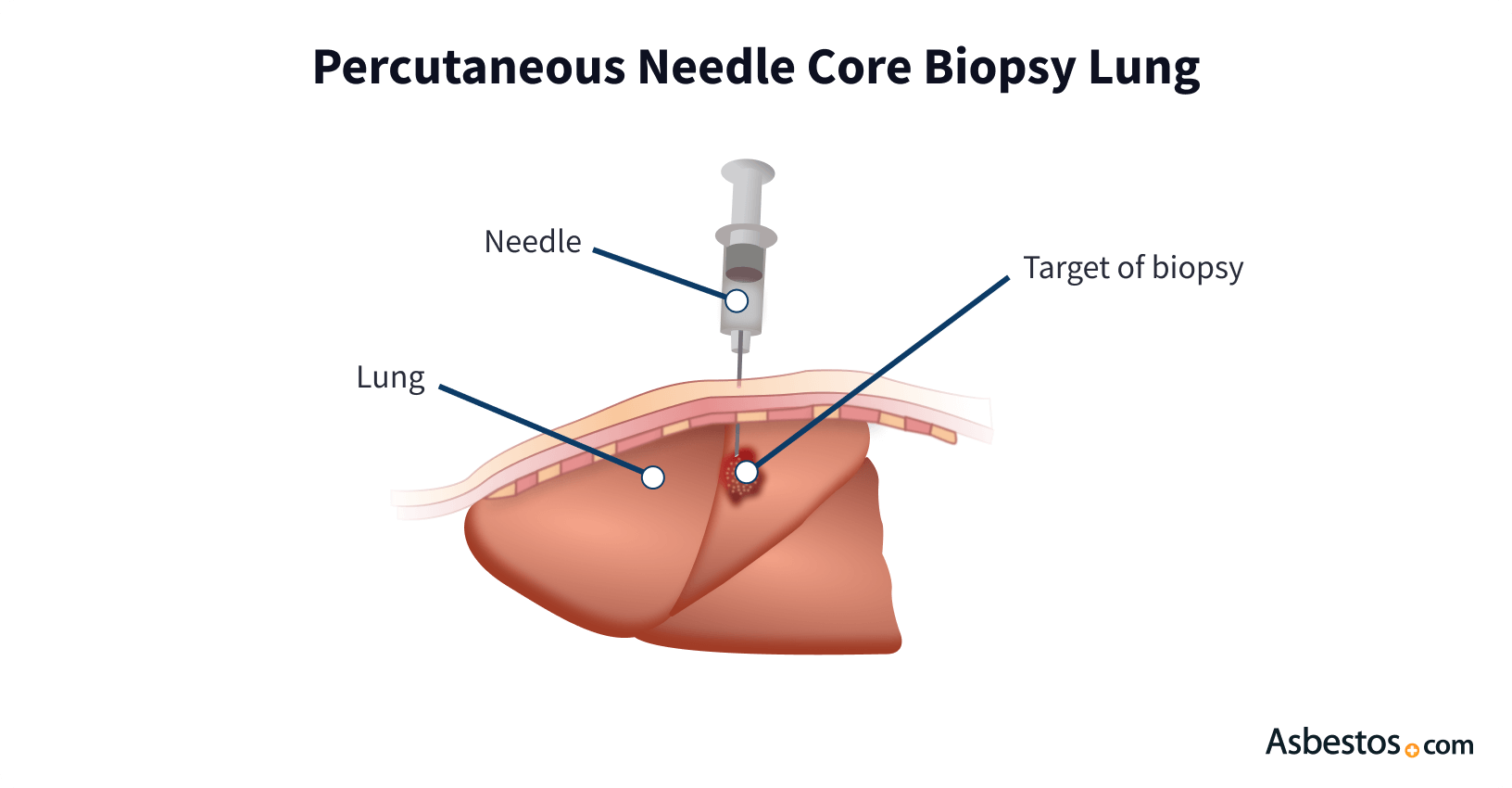
This method is less risky than endoscopy. But, patients still face a small risk of infection or bleeding. Lung biopsies can cause a collapsed lung or blood pooling around the lung (hemothorax). Coughing up a small amount of blood after a lung biopsy is normal.
Fine-Needle Biopsy Procedure
Before a fine-needle biopsy, talk to your doctor about what to expect. You may need to take medication for pain or anxiety before the procedure. It depends on your needs and health.
- Preparation: Your doctor will clean your skin and apply a local anesthetic to numb the area. Then, they will position you for easy access to the biopsy site.
- Procedure: Your doctor will use ultrasound or CT scans for guidance. They will insert a needle into the chest or abdomen to extract samples. The entire process usually takes less than 10 minutes.
- Post-Procedure Care: After removing the needle, your doctor will clean and bandage your incision. It won’t require stitches.
- Sample Analysis: Your doctor sends the tissue samples to a pathology lab. Results usually take several days to a week or more.
You can go home after the procedure. Experiencing some pain is normal. The patient may take OTC pain meds, per the doctor’s instructions. They should rest and limit activity for several days.
Thoracentesis and Paracentesis
Thoracentesis and paracentesis are 2 other procedures that aren’t true biopsies, but they’re similar. Thoracentesis drains fluid from around the lungs. Paracentesis drains fluid from the abdomen.
Your doctor will use local anesthesia. They will insert a long, blunt needle to drain fluid from the lining of the lung or abdomen. Lab tests help them determine the cause of your excess fluid.
Neither procedure can accurately diagnose mesothelioma. But, they can aid diagnosis. Many other conditions cause excess fluid, so it’s important to rule them out. Removing fluid relieves symptoms of pleural effusion such as shortness of breath. It also improves abdominal swelling associated with ascites.
Surgical Mesothelioma Biopsies
Doctors don’t typically use surgical biopsies to diagnose mesothelioma. If an endoscopic or fine-needle biopsy isn’t possible, the patient may need surgery to find and biopsy tumors.
A surgeon performs a surgical biopsy during open surgery. This lets the doctor see any tumors and collect large samples, including whole tumors. The type of biopsy a patient needs depends on the mesothelioma’s location.
Types of Surgical Biopsies for Mesothelioma
- Laparotomy: A laparotomy is an exploratory surgery where doctors open the abdomen. This procedure helps to diagnose peritoneal mesothelioma.
- Thoracotomy: A thoracotomy opens the chest cavity or pleural space around the lungs.
When performing a surgical biopsy, the surgeon will usually remove as much of the suspected cancer as possible. This provides a large sample of cancer cells for testing. It has the highest accuracy for diagnosing mesothelioma. But, it also has the greatest risk of complications.
Surgical biopsies require general anesthesia and large incisions. Any major surgery carries a high risk of bleeding, infection or other complications. Surgical biopsies require much more recovery time than less-invasive ones.
The experience of the pathologist reviewing the biopsies is very important. It’s important that the biopsies get reviewed by a hospital or a medical center that has a pathologist who specializes in mesothelioma and examines a lot of samples.
How You Can Prepare for a Mesothelioma Biopsy
Preparing for a mesothelioma biopsy varies by type. Your doctor will give detailed instructions.
Tips to Prepare for a Biopsy
- Follow Pre-Procedure Instructions: Leave valuables at home, remove jewelry and wear comfortable clothing. Follow any specific instructions about fasting before your procedure.
- Medication Management: Tell your doctor about all medications you take. This includes over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements and vitamins. If you’re on blood thinners (e.g., coumadin, heparin or aspirin), your doctor may advise you to stop taking them temporarily to reduce the risk of bleeding.
- Day of Your Procedure: If receiving general anesthesia, arrange for a ride to and from your procedure. Without a companion, the procedure may not be performed. If you plan to stay overnight, bring a bag with essentials. Pack a change of clothes and a phone charger.
- Aftercare and Results: Ask about aftercare and when to expect biopsy results.
One of the most important steps in preparing for a procedure is to ask questions and get answers. It can help to give permission for your healthcare team to talk to a loved one about recovery. Anesthesia following your biopsy may affect your memory.
Understanding Your Biopsy Results and Next Steps
After your biopsy, you and your doctor will get a report with the results. A biopsy can find the subtype of mesothelioma, if it has spread and other details. Doctors use this information along with scans to find the mesothelioma stage. They choose the best treatment based on the test results.
You can discuss how the results will impact treatment with your doctor. Both your doctor and the pathologist must be experienced with mesothelioma to interpret the results. Communicating well with your doctor is important. You can prepare questions and communication strategies to speak with doctors about biopsy results and the next steps.
Coping with a mesothelioma diagnosis is a challenge, but it is one you do not have to face alone. The Mesothelioma Center is here to provide the support that survivors need.
Recommended Reading






