Biphasic Mesothelioma
Biphasic mesothelioma is a cancer caused by exposure to asbestos. Malignant biphasic tumors have two types of cells: epithelioid and sarcomatoid. Symptoms of biphasic mesothelioma can include a dry cough, shortness of breath and fluid in the lungs. Biphasic mesothelioma is sometimes referred to as mixed mesothelioma.
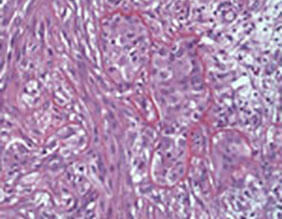
What Is Biphasic Mesothelioma?
Biphasic mesothelioma is a subtype of mesothelioma named for the specific mix of cells found in tumors. Biphasic means there’s a mix of both types of mesothelioma cells: epithelial and sarcomatoid cells. Pathologists can see these cells when they look at tissue samples under a microscope during a biopsy.
The presence of both cell types makes biphasic mesothelioma more complex than the other subtypes. The amount of epithelial versus sarcomatoid cells you have can affect your prognosis. Having more epithelioid than sarcomatoid cells usually leads to better outcomes.
Biphasic Mesothelioma Characteristics
- Cell mix: There must be at least 10% of both cells for a biphasic mesothelioma diagnosis.
- Epithelioid cells: These cells are cube-shaped, closely packed and slower to spread, making them more responsive to treatment.
- Sarcomatoid cells: They’re spindle-shaped, loosely arranged and more aggressive, leading to faster disease progression and resistance to treatment.
The biphasic subtype accounts for approximately 20% to 35% of all mesothelioma cases. Because of its mix of both sarcomatoid and epithelioid cells, biphasic mesothelioma is known for varying degrees of tumor aggression and treatment response. A personalized treatment plan is needed to best manage both cell types.
Exposure to asbestos is the only known cause of biphasic mesothelioma. As with all mesothelioma types, inhaled asbestos fibers can become stuck in the lining of the lungs or abdomen, causing irritation that can lead to cancer.
Symptoms of Biphasic Mesothelioma
Symptoms of biphasic mesothelioma include dry cough, shortness of breath and fatigue. These symptoms vary depending on where tumors have developed in the body.
Common Symptoms of Biphasic Mesothelioma
- Chest or abdominal pain
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss
- Fluid buildup in the lungs or abdomen (pleural or peritoneal effusion)
- Persistent dry cough
- Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing
Research also indicates people with more sarcomatoid cells may experience more severe and frequent symptoms. The cancer progresses faster and is more likely to recur with this subtype.
Early symptoms for biphasic mesothelioma are often vague and resemble less severe conditions, which can delay diagnosis. This delay is why it’s crucial to recognize mesothelioma symptoms early for better treatment outcomes.

Understand your diagnosis, top doctors and ways to afford care.
Get Your Free GuideHow Is Biphasic Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
Accurately diagnosing biphasic mesothelioma requires a combination of imaging tests, biopsies and pathology evaluations. Because its symptoms overlap with those of other conditions, misdiagnosis can occur without a thorough assessment.
Biphasic Mesothelioma Diagnostic Steps
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans and MRIs help detect tumors, as well as assess their size and identify fluid buildup.
- Biopsy: Pathologists analyze tissue samples and determine the proportion of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells. A biopsy is the only way to definitively diagnose biphasic mesothelioma.
- Pathology review: Experts examine biopsy samples under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Dr. Andrea Wolf, director of the New York Mesothelioma Program at Mt. Sinai, tells us, “If more than 90% of one cell type is present, it’s termed ‘pure.’ For instance, having more than 90% epithelioid cells indicates epithelial type. If both types are represented, it’s biphasic or mixed.”
A case study in Cureus discussed a 34-year-old male who was initially misdiagnosed with peritoneal tuberculosis. After multiple CT scans and specialist pathology studies, he received an accurate diagnosis of biphasic peritoneal mesothelioma 5 weeks after his initial symptoms.
How Is Biphasic Mesothelioma Treated?
Treatment for biphasic mesothelioma often includes chemotherapy or surgery. A combination of different therapies is often recommended.
Several factors that can affect the best treatment plan for you include the proportion of cell types present, your overall health and the stage of the disease. These factors can indicate how well you might respond to each treatment.
Biphasic Treatment Options
- Chemotherapy: Drugs like cisplatin and pemetrexed are commonly used to slow tumor growth and improve symptoms for people with more epithelial cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting your immune system with drugs like Opdivo and Yervoy can help your body fight cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: This helps shrink tumors, reduce recurrence and alleviate symptoms like pain and breathing difficulties.
- Surgery: Those with more epithelioid cells or in early stages of mesothelioma may benefit from tumor removal procedures.
Treating biphasic mesothelioma is difficult. However, new medical research is helping improve results. Anna Nowak, Ph.D., a premiere asbestos researcher, tells us Opdivo and Yervoy “can double survival” for people with sarcomatoid and biphasic mesothelioma.
A personalized treatment plan that considers the specific details of your health can lead to better care. Ask your mesothelioma doctor about your choices, including clinical trials.
Biphasic Prognosis and Life Expectancy
The prognosis for biphasic mesothelioma is generally poor, but every individual may respond to treatment differently. Many factors can affect someone’s outcomes including overall health and the stage of the disease at diagnosis.
The amount of each cell type in biphasic or mixed mesothelioma also makes a difference. Sarcomatoid cells can make this subtype more difficult to treat. Overall, people live an average of 10 months after diagnosis, but those with mostly epithelioid cells tend to survive longer.
| Cell Type Ratio | 1-Year Survival Rate | 3-Year Survival Rate | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mostly Epithelioid | 60% | 25% | 10% |
| Mixed | 45% | 15% | 5% |
| Mostly Sarcomatoid | 30% | 5% | <1% |
Common Questions About Biphasic Mesothelioma
- What causes biphasic mesothelioma?
-
Asbestos exposure is the leading cause of biphasic mesothelioma. When asbestos fibers are inhaled or ingested, they become lodged in organ linings. This can lead to chronic inflammation and cancerous mutations over time.
- Can biphasic mesothelioma be misdiagnosed?
-
Yes, biphasic mesothelioma is frequently misdiagnosed as lung cancer or other mesothelioma subtypes. A biopsy and pathology review are essential for accurate diagnosis.
- What are the early warning signs of biphasic mesothelioma?
-
Early signs include shortness of breath, chest or abdominal pain, persistent cough, and unexplained weight loss. Symptoms may be mild initially but worsen as the disease progresses.
- How long does biphasic mesothelioma take to develop?
-
Biphasic mesothelioma can take 20-60 years to develop after asbestos exposure. This long latency period makes early detection difficult, emphasizing the importance of regular health screenings for at-risk individuals.




