Types of Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma types describe where tumors start: Pleural in the lung lining; peritoneal in the belly lining; pericardial around the heart; and testicular in the testes lining. Cell types define subtypes. Epithelioid is easier to treat. Sarcomatoid is aggressive. Biphasic is a mix of both cell types.
What Are the 4 Types of Mesothelioma?
Mesothelioma has 4 main types, based on where the cancer starts in the body. All types begin in the mesothelium, a thin layer of tissue that covers organs and body spaces. Asbestos exposure can damage the mesothelial cells in this lining and turn them into cancer.
The 4 Types of Mesothelioma
- Pleural mesothelioma: This type forms in the lungs’ lining (pleura).
- Peritoneal mesothelioma: This type starts in the abdominal lining (peritoneum).
- Pericardial mesothelioma: This rare type develops in the heart’s lining (pericardium).
- Testicular mesothelioma: This rare type forms on the lining of the testes (tunica vaginalis).
Dr. Andrea Wolf, director of the Women’s Lung Cancer Program at Mount Sinai, tells us, “Plural mesothelioma comes in two general varieties. There is something called ‘epithelial cell type,’ which is a little more favorable. It’s associated with better survival and is more common. And there’s something called ‘sarcomatoid mesothelioma,’ which is a little bit more difficult to treat and patients have a worse prognosis.”
Pleural Mesothelioma
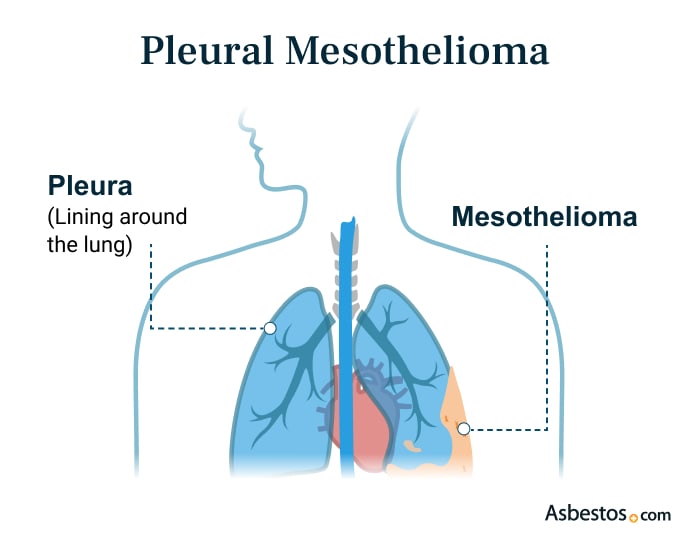
Pleural mesothelioma is a cancer that starts in the lining of the lungs. It makes up most mesothelioma cases, about 75% to 80%. If you have chest pain, trouble breathing, tiredness, fever or weight loss, see a doctor. Finding it early can lead to better treatment. Doctors use exams, scans, fluid tests and a biopsies to diagnose it. Be sure to tell your doctor if you’ve been exposed to asbestos.
Doctors often treat early-stage pleural mesothelioma with immunotherapy, chemotherapy, surgery and radiotherapy. People treated in stage 1 may live around 3 years or more, while stage 4 patients usually live about 12 months. However, pleural mesothelioma survivors who have lived for decades after their diagnosis and treatment have shared their firsthand stories with us. Each person is an individual. Clinical trials also offer new treatment options and have helped people achieve better outcomes.
Michael Cole, a 10-year pleural mesothelioma survivor, shares his experience with treatment and recovery. He tells us, “If we remain in denial about our condition or allow doubt and fear to rule our decision-making, it will undermine our treatment plan. Anger, cynicism, anxiety and depression can drastically affect our ability to continue on a path to recovery. Mesothelioma treatments can be tough, and things may look bad, but there is hope. Don’t give up!”

Understand your diagnosis, top doctors and ways to afford care.
Get Your Free GuidePeritoneal Mesothelioma
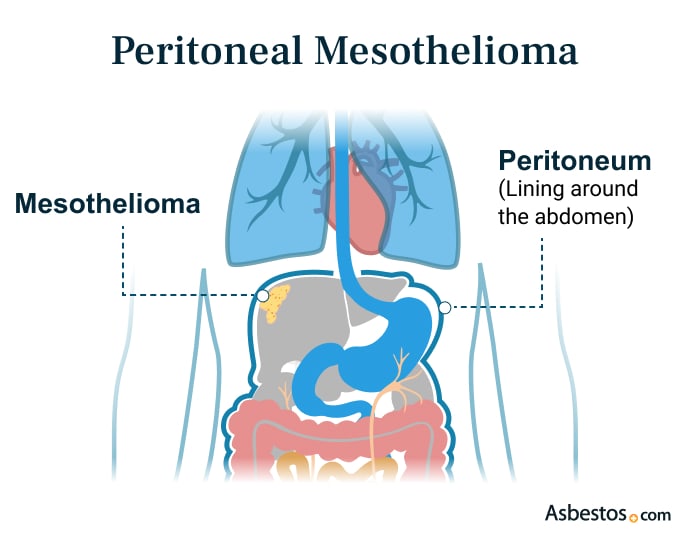
Peritoneal mesothelioma starts in the lining of the belly, which protects your stomach and other organs. This type of mesothelioma makes up about 10% to 30% of all cases. Common symptoms include belly pain, swelling, bloating, loss of appetite and changes in bowel habits. If you notice any of these signs, talk to a doctor for help and advice.
Doctors often treat peritoneal mesothelioma with a combination of surgery and heated chemotherapy. About 50% of patients can get this treatment, and many of them live 5 years or longer after diagnosis. Even though people with peritoneal mesothelioma usually have a better outlook than those with pleural mesothelioma, doctors still need to do more research to improve care. Some doctors use immunotherapy combinations, but that treatment is not FDA-approved.
Pericardial Mesothelioma
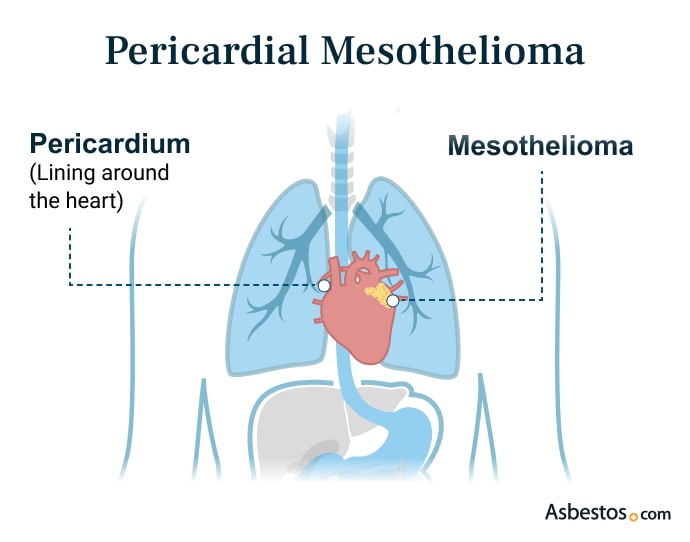
Pericardial mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that grows in the sac that protects the heart called the pericardium. Doctors have only reported about 200 cases. People with this very rare cancer might feel chest pain, have an irregular heartbeat, cough a lot or have trouble breathing.
Doctors may treat pericardial mesothelioma mostly with surgery and chemo. A 2022 report in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology showed patients who got a mix of these treatments lived a median of 25.9 months. Those who received both types of treatment, called bimodal therapy, lived a median of 70 months. To choose the best treatment for you, talk with your doctor about every option.
Testicular Mesothelioma
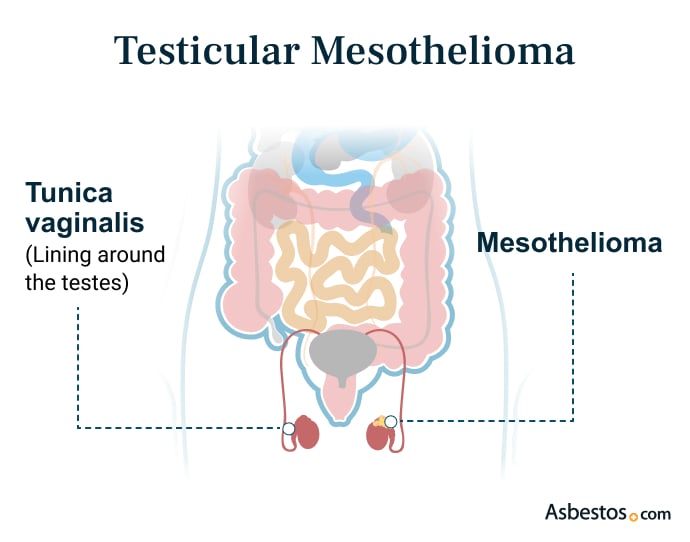
Testicular mesothelioma is a very rare cancer that starts in the outer lining of the testes or tunica vaginalis. Doctors have reported fewer than 300 cases, which accounts for fewer than 1% of all mesothelioma cases.
People with testicular mesothelioma may notice swelling in the scrotum or painless lumps. Doctors often treat it with surgery and chemotherapy. Some patients may also join clinical trials to try new treatments. With these options, many people live for more than 2 years after diagnosis.
Mesothelioma Cell Types
In addition to the 4 main types of mesothelioma, there are 3 subtypes based on cell types. The types of mesothelioma cells are: epithelioid, sarcomatoid and biphasic. Biphasic is a combination or mix of epithelioid and sarcomatoid.
Epithelioid mesothelioma cells are the most common type. This subtype makes up about 70% to 75% of all cases. The sarcomatoid cell type is the least common among mesothelioma subtypes, making up about 10% to 20% of all diagnoses. Approximately 30% of pleural tumors and 25% of peritoneal tumors are classified as biphasic.
Dr. Andrea Wolf explains, “If there’s more than 90% of one cell type, it’s referred to as ‘pure’ of that cell type. So somebody with more than 90% epithelioid cell type under the microscope is considered epithelial. But if there is a representation for both cell types, that’s called biphasic or mixed cell.”
Epithelioid Cells
Epithelioid mesothelioma cells often look like ovals or cubes and tend to clump together, which helps doctors spot them under a microscope. These cells usually grow slower and respond better to treatment than other types.
Mesothelioma specialists take cell types into account when they develop a treatment plan with you. The aim is to match you with the therapy option that will fight your specific type best. The responsiveness of epithelioid mesothelioma to treatment is good news for patients, as those with epithelioid cell tumors often have a better outlook.
Sarcomatoid Cells
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma cells are long and spindle-shaped, like stretched-out ovals. You might hear this cell type referred to as sarcomatous, spindle or diffuse malignant fibrous mesothelioma. It’s also known as the most aggressive cell type.
These cells often grow in loose patterns instead of clumps. This makes sarcomatoid mesothelioma harder to treat, as the cells spread quickly through the body and respond poorly to most treatments.
Biphasic Cells
Biphasic mesothelioma has a combination of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells. The cancer’s behavior depends on which cell type is more dominant in the tumor. Tumors with more epithelioid cells tend to grow slower and respond better to treatment. When sarcomatoid cells are dominant, the cancer is often harder to treat and more aggressive.
People with biphasic mesothelioma often have a better outlook if a tumor has more epithelioid cells. But as Dr. Wolf tells us, “People shouldn’t take the prognosis associated with their cell type as a hard and fast rule about how long they’re going to live.”

Access trust funds and grants to ease the cost of your treatment.
Get Help NowTreatment by Type of Mesothelioma
When developing your mesothelioma treatment plan, your doctor will consider your mesothelioma type and cell type. This is why a precise mesothelioma diagnosis is such a key part of developing a personalized treatment plan. Your doctor will also consider your age, overall health and treatment goals.
A multimodal or combined therapy approach has been shown to usually yield the best results for mesothelioma survivors. If you’re younger and in good health, surgery might be a good choice. Many patients can also benefit from chemo, radiation or immunotherapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemo treats several types of mesothelioma. For pleural mesothelioma, doctors often use a mix of cisplatin and Alimta (pemetrexed). This combination slows the growth of tumors and improves symptoms.
For peritoneal mesothelioma, doctors may use drugs like Gemzar (gemcitabine) or Paraplatin (carboplatin). Paraplatin is sometimes heated and placed directly into the abdomen during heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy or HIPEC. In our exclusive 2025 survey of mesothelioma survivors, participants who reported remission were 31% more likely to have received Paraplatin than those who didn’t.
Surgery
Doctors use different surgery options for mesothelioma, depending on where the cancer starts. Surgery works best for younger patients in good health who catch the disease early. Sometimes, only tumors or affected tissues are removed. However, procedures such as extrapleural pneumonectomy remove the whole lung and nearby tissue.
Surgeons also perform a pleurectomy to remove the lining around the lungs or remove chest tumors through decortication when treating pleural patients. To treat peritoneal patients, surgeons often remove tumors from the belly lining and sometimes nearby organs like the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas or spleen during a peritonectomy.
To treat pericardial mesothelioma, doctors can remove the sac around the heart with a pericardiectomy. For testicular mesothelioma, surgeons usually remove the testicle in a surgery called an inguinal orchiectomy.
| Pleural Mesothelioma Stage | Percentage of Patients Opting for Surgery |
|---|---|
| Stage 1 | 20% |
| Stage 2 | 22% |
| Stage 3 | 14% |
| Stage 4 | 11% |
Immunotherapy
In 2024, the FDA approved the immunotherapy drug Keytruda (pembrolizumab) in combination with the chemo drugs Alimta and Platinol or Paraplatin as a first-line treatment for pleural mesothelioma. This followed the agency’s 2020 approval of Opdivo (nivolumab) and Yervoy (ipilimumab) together as a first-line therapy for pleural patients.
Today, immunotherapy for pleural mesothelioma is an established treatment with positive results. While not specifically FDA-approved as a first-line treatment for other mesothelioma types, some specialists are seeing benefits of this therapy for their patients.
Radiation Therapy
Doctors often combine radiation with surgery to slow tumor growth in people with pleural mesothelioma. Radiation therapy for mesothelioma on its own can shrink tumors and relieve symptoms, which helps many patients feel better.
This therapy isn’t commonly used for peritoneal mesothelioma because it might affect organs like the kidneys or liver. Radiation is also uncommon for pericardial mesothelioma because of the potential risk of damage to the heart.
There’s less data to support radiation for testicular mesothelioma, and its use is less common than for pleural patients. But radiation may be part of a multimodal plan for this type of mesothelioma.
Palliative Therapy
Palliative therapy controls the pain and other symptoms cancer can cause. It plays an important role in your treatment plan and can improve how you feel and live.
One common palliative treatment for mesothelioma is thoracentesis, where doctors drain excess fluid around your lungs to help you breathe more easily. Another helpful option is paracentesis, which removes fluid from your belly to ease pressure and make eating more comfortable. These treatments can help you feel better and enjoy a better quality of life.
- A 2024 report says peritoneal patients in a study had a lower overall response to Keytruda than pleural mesothelioma patients did. This highlights the role mesothelioma type can play.
- Individual factors also matter. The 2024 report discusses a peritoneal patient who is 4 years disease free following 2 years of Keytruda. Discuss your options with your doctor.
“The type of mesothelioma a patient has plays a critical role in determining the best approach. Treatment options can vary significantly based on tumor type and characteristics, which is why patients need to understand how their medical team tailors recommendations to their specific diagnosis rather than applying a one-size-fits-all approach.”
Common Questions About the Types of Mesothelioma
- What is the difference between mesothelioma cell types and tumor location?
-
Cell type refers to the type of cells that make up the tumors. Tumor location refers to where the cancer first began growing, such as the lining of the lungs or abdomen.
- How does the type of mesothelioma impact prognosis and treatment?
-
The type of mesothelioma a patient has impacts their overall prognosis and recommended treatments. Mesothelioma treatment is complex, and many other factors influence treatment options and prognosis, such as the stage of the cancer.
- How can I find a mesothelioma specialist for my type of mesothelioma?
-
You can speak with a Patient Advocate to find a mesothelioma specialist who has experience treating your type of mesothelioma.
- Can someone have more than one type of mesothelioma?
-
Yes, a person can develop more than one type of mesothelioma, but it’s very rare. Having more than one type can make diagnosis and treatment more complex. Working with a mesothelioma specialist can ensure you get the care you require.








