Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
Desmoplastic mesothelioma is a rare cell subtype of sarcomatoid malignant mesothelioma. Asbestos exposure is the primary cause. Symptoms include chest pain and fluid buildup in the lungs. Doctors use biopsies to diagnose desmoplastic mesothelioma.
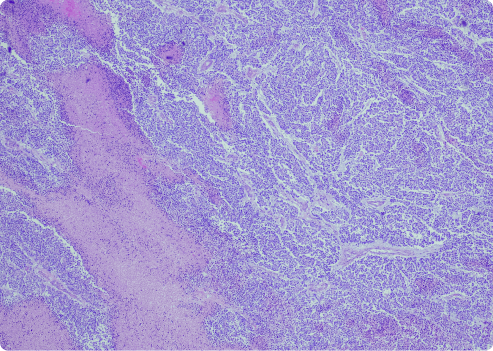
What Is Desmoplastic Mesothelioma?
Desmoplastic mesothelioma is a unique type of sarcomatoid mesothelioma. The term “sarcomatoid” describes long, spindle-shaped cells. This subtype is rare. It can be more aggressive than other forms of mesothelioma.
This variant has dense fibrous tissue and fewer cells. Desmoplastic cells are hard to identify. They lack clear patterns. These types of mesothelioma cells form dense nodules of connective tissue in tumors. This can make diagnosis more difficult.
Key Facts About Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
- Desmoplastic mesothelioma is hard to diagnose. Its tissue structure is dense and fibrous. It can resemble similar benign conditions.
- Doctors use imaging scans and biopsies for an accurate diagnosis. Pathologists test biopsied tissue and look for signs of desmoplastic cells.
- Desmoplastic cells, like other sarcomatoid cells, are hard to treat. This negatively impacts survival rates.
- In clinical trials, immunotherapy and targeted therapy show promise for desmoplastic cell types.
Unfortunately, it tends to have a poor outlook and can appear in all types of sarcomatoid mesothelioma. It’s observed in 5% to 10% of all malignant mesothelioma cases.
“Most patients don’t know their cell type when I initially speak with them,” says Dr. Snehal Smart, a Patient Advocate at The Mesothelioma Center. “I help them review their pathology report and explain what sarcomatoid cell types are and what this means for them.”
What Causes Desmoplastic Mesothelioma?
The main cause of this disease is exposure to asbestos. It can develop in various types of mesothelioma cancer.
Studies show an association between heavy asbestos exposure and sarcomatoid mesothelioma. One study of 180 desmoplastic cases found much higher levels of amosite asbestos fibers in analyzed samples from sarcomatoid tumors.
What Are the Symptoms of Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
The most common symptoms include pain, breathing problems and cough. Dense and fibrous areas in the lungs can lead to pulmonary fibrosis that causes shortness of breath.
Common Symptoms of Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
- Anemia (low iron)
- Chest pain or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen
- Coughing up blood
- Fatigue and extreme tiredness
- Loss of appetite, nausea, and anorexia
- Low blood oxygen levels
- A persistent cough
- Prolonged hoarseness
- Shortness of breath
- Weight loss and weakness
The type of tumor cells doesn’t change the symptoms of mesothelioma. For example, people with pleural mesothelioma often feel short of breath. Abdominal pain may occur in those with peritoneal mesothelioma. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult a health care professional.

Understand your diagnosis, top doctors and ways to afford care.
Get Your Free GuideHow Do Doctors Diagnose Desmoplastic Mesothelioma?
A biopsy is the most common method doctors use to diagnose desmoplastic mesothelioma. A biopsy helps determine the cell type and the best treatment options.
Criteria for Diagnosing Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
- At least 50% of the tumor consists of nodules with dense fibrous tissue.
- Areas with increased cell activity show sarcomatoid features.
- Neoplastic spindle cells have spread to the lungs or chest wall.
- There is evidence of metastasis to nearby fat tissue, skeletal muscle or the lungs.
- The p53 tumor suppressor gene protein is present.
When desmoplastic mesothelioma spreads, it can seem less aggressive. This makes it easy for doctors to mistake the cells for benign fibrous tissue. Imaging scans, like CT or MRI, can be very helpful for pathologists. It can make it easier to spot the spread of tumors and correctly diagnose tough cases.
Misdiagnoses
The fibrous parts of this type of tumor can sometimes hide variations in the cells. This can block an accurate diagnosis.
Doctors have mistaken desmoplastic pleural mesothelioma for fibrous pleurisy. Other possible misdiagnoses include: Pleural fibrosis, rheumatoid disease or spindle cell sarcoma.
One way to tell desmoplastic mesothelioma apart from sarcomatoid lung cancer is the GATA-3 protein. It’s often present in many mesothelioma cases. But it’s usually absent in lung carcinoma cases. This also helps doctors stage pleural mesothelioma.
What Are the Treatment Options for Desmoplastic Mesothelioma?
Doctors treat desmoplastic mesothelioma with immunotherapy, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. These treatments kill cancer cells, shrink tumors and stop their spread. They ease symptoms, extend life and improve patients’ lives.
One of the most promising first-line treatments is Opdivo with Yervoy. A 2022 study highlighted Opdivo might be particularly effective for sarcomatoid cells. They often have higher levels of a particular protein, PD-L1. This protein makes the cells more receptive to immunotherapy.
Following this, chemo with cisplatin and Alimta is commonly used. Radiation therapy can also be beneficial. It’s especially helpful for reducing painful tumors in the chest wall.
Surgery to remove tumors isn’t usually recommended for this type of mesothelioma. It has a high risk of recurrence within a few months. Some early-stage patients have had better outcomes. Doctors often suggest minor surgeries to drain excess fluid. These include pleurodesis or paracentesis.
Desmoplastic Mesothelioma Prognosis and Survival
The prognosis for mesothelioma with desmoplasia is poor. This cell type tends to spread rapidly. Many patients find their disease is already advanced when they receive a diagnosis.
The sarcomatoid cell type is also the most aggressive and least treatable subtype of mesothelioma. Their shape and behavior make these cells resistant to chemo and radiation. The cancer’s resistance to therapy and its advanced stage at diagnosis limits treatment options. Unfortunately, this can lead to a life expectancy of less than 1 year for those affected.
Genetic and molecular research may offer hope. Emerging therapies, like immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show promise in clinical trials.
Survival Rates
Survival rates range from 4 to 12 months after diagnosis. Studies have reported a median survival of 3.8 months with 1 patient living 11.5 months.
A historic 7-year study looked at 255 patients with mesothelioma from 1982 to 1989. Researchers found 17 cases of the desmoplastic subtype. Among these, 11 were pure sarcomatoid and 6 were biphasic. The biphasic type has both sarcomatoid and epithelial cells. The average survival time was about 5.8 months for the pure sarcomatoid variant and 6.8 months for the biphasic variant.
These statistics can feel overwhelming. It’s important to seek support and explore treatment options. Every patient’s journey is unique. There are resources available to help navigate this difficult time.
Common Questions About Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
- Can desmoplastic mesothelioma develop without asbestos exposure?
-
Asbestos exposure is the primary cause of desmoplastic mesothelioma. Though not every patient with the disease has a known history of exposure.
- What support resources are available for families of patients with desmoplastic mesothelioma?
-
Support includes counseling, financial aid and transportation. There are also resources offering help around the house. Families can access support resources a number of ways. These include: Support groups, social workers, therapists, cancer centers and non-profit organizations.
- Are there alternative therapies for desmoplastic mesothelioma?
-
No alternative therapy has proven successful for any type of mesothelioma. Some patients do report complementary therapies help them manage their symptoms. Immunotherapy drugs, however, are helping people with desmoplastic mesothelioma live longer.
- Can desmoplastic mesothelioma spread to other parts of the body?
-
Yes, desmoplastic mesothelioma has the potential to spread to other parts of the body. All cell types of mesothelioma tend to spread locally before traveling far from their origin. Sarcomatoid cell types tend to spread quicker than epithelioid cells.






