
Connect with top-rated doctors specializing in mesothelioma treatment, who will personalize treatment options based on your diagnosis.
Find Your SpecialistEpithelioid, sarcomatoid and biphasic are the three main types of mesothelioma cells. Epithelioid is the most common type and offers the best prognosis. Meanwhile, sarcomatoid is rare and has a poor prognosis. Biphasic has a mix of both cell types, and prognosis depends on the ratio of each.
Mesothelioma tumors contain either epithelial, sarcomatoid or biphasic cells. Each type of mesothelioma cell influences how the tumor grows and responds to treatment. Identifying your mesothelioma cells empowers you and your doctor to make informed decisions to customize a treatment plan for you.
Key Facts About Mesothelioma Cells
The most common cell type in mesothelioma cases is epithelioid, which makes up 50% to 70% of cases. They often form clusters or sheets of oval or cube-shaped cells with clear centers visible under a microscope. Sarcomatoid is rarer with spindle-shaped cells. Biphasic is a mix of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells. There are also a few rare subtypes, but most cases fall into these three categories.
Studying mesothelioma cells and tissues under a microscope is called histology, which helps show their structure and behavior. Histology reveals key details about these mesothelioma cells, which are noted in your pathology report.
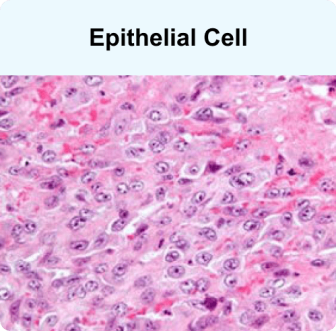
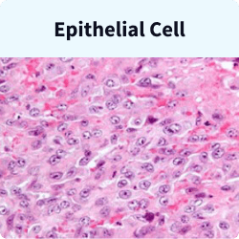
Epithelial or epithelioid mesothelioma cells are typically uniform with growth patterns that are somewhat predictable. Those with an epithelial cell type tend to have a better outlook or prognosis. These tumors aren’t as aggressive and respond well to intensive treatment regimens like surgery and chemo.
Christine Shippen, a pleural mesothelioma survivor who was diagnosed with this specific type of mesothelioma, shared her advice for other survivors with us. She said, “Be advised by your doctor or oncologist what the best treatment is for you. There are other treatments available depending on how fit you are.”
Reflecting on her 6 years as a survivor, she added, “Give yourself time to come to terms if you can. The longer I live, I continue to thank God for giving me the willpower to believe I will fight the fight to the end. My perspective remains always positive.”


Sarcomatoid mesothelioma cells occur in only about 10% to 20% of cases. They’re generally associated with poor outcomes, though everyone responds to treatment differently. This is the most aggressive cell type. This can make treating sarcomatoid mesothelioma more challenging.
Sarcomatoid cells develop quickly and don’t respond as well to typical treatments. They may need more aggressive treatment protocols, and people with this cell type are often diagnosed at later mesothelioma stages.
Diagnosed with the sarcomatoid mesothelioma subtype, Wally Rogers far surpassed his initial prognosis. After experiencing serious side effects from chemo, Wally tells us he tried Keytruda, saying, “It’s a real mystery at this point why I’ve done so well. After listening to the medical people, it’s almost shocking. I’m not superhuman by any means. I’m a simple man. Maybe I can let people know, there is hope out there.”

Connect with top-rated doctors specializing in mesothelioma treatment, who will personalize treatment options based on your diagnosis.
Find Your Specialist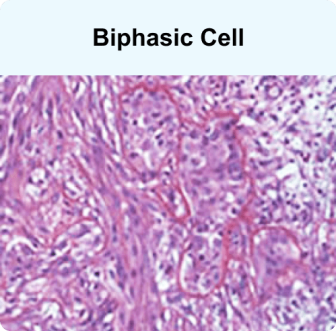
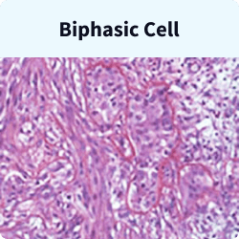
Biphasic mesothelioma cells are a combination of epithelial and sarcomatoid cells. This mixed cell type accounts for 20% to 30% of mesothelioma cases. To receive a biphasic diagnosis, each cell type must account for at least 10% of the tumor mass.
Since biphasic tumors consist of mixed cell types, they can be challenging to accurately diagnose based on smaller biopsies. Your treatment plan and outlook depend on which type is found in greater amounts in your biopsy sample.
Registered Nurse and Patient Advocate Karen Selby explains, “Cisplatin and carboplatin combination is usually the gold standard” for people with epithelioid mesothelioma cells. However, for people with sarcomatoid and biphasic mesothelioma cells, “immunotherapy is often the go to now.”
Some mesothelioma tumors contain rare subtypes that don’t fall into one of the main categories. These unusual mesothelioma cell types can make diagnosis more complex and may influence how the cancer responds to treatment.
Rare Forms of Mesothelioma Cell Types
These rare cell types often require advanced pathology testing. While there is no specific treatment protocol for each, doctors base treatment decisions on the cells’ dominant behavior and whether they act more like epithelial or sarcomatoid mesothelioma.
To find out your specific mesothelioma cell type, pathologists take a small piece of tissue from a biopsy. They look at it under a microscope using chemical stains that make the cells’ features stand out. They study the cells to see what they look like and how they function.
Special tests, like immunohistochemistry, help doctors find specific markers on the cells. Knowing the cell type helps cancer doctors diagnose mesothelioma and choose the best treatment plan based on how the cancer might behave.
Pathologists use special tests and advanced tools to study mesothelioma cells. These methods show detailed features of the cells’ structure, genes and proteins. They also reveal how the cells grow, change shape and interact with their surroundings. This helps doctors understand how aggressive the cancer might be, how it behaves and how it may respond to different strategies.
Tools for Studying Mesothelioma Cells
All of these assessments help to create a more complete understanding of mesothelioma cells. Your doctors use this information to understand how each individual mesothelioma case operates on a cellular level and develop a treatment plan that works best for you.

Get answers about treatment, top doctors, and clinical trials from the nation’s most trusted mesothelioma resource.
Get Your Free GuideMesothelioma cell types affect outcomes because they change how cancer cells and their surroundings behave. Slower-growing types like epithelioid respond better to surgery and medicines because their tumors let treatments and the immune system work more easily. Faster-growing types like sarcomatoid build thick tissue that blocks treatment and immune system defenses, making them harder to treat. These differences also affect how well newer treatments, like immunotherapy, work.
When doctors look at biopsy results, they can decide if surgery is a good option or if relieving symptoms with palliative care is better. These results also help doctors and patients have clearer conversations about what’s ahead, allowing them to prepare with their families for their mesothelioma journey.
New treatments are helping some people with mesothelioma live longer. In a 2025 study in the International Journal of Clinical Oncology, immune checkpoint inhibitors Opdivo and Yervoy improved progression-free survival for almost 11 months in some people. Overall survival was significantly better in patients with the epithelial cell type.
Healthy mesothelial cells are those that line the lungs, the abdomen and the heart sac. They become malignant cancerous cells through asbestos exposure, which irritates the lining and instigates tumor growth.
Yes. Biphasic mesothelioma has both epithelial and sarcomatoid cells within one tumor. The dominant type will determine the characteristics of the cancer and the treatment.
Generally, no. People with mesothelioma usually don’t have a different type over the course of their treatment or disease. Treatment response and the way tumors develop may vary throughout the progression of mesothelioma.
Both mesothelioma cell type and how far the cancer has spread are important. Cell type informs aggressiveness and response to treatment, while stage indicates the ability to spread. They factor into prognosis upon first diagnosis and affect the care you’ll receive.
Stay up-to-date on treatment, research, clinical trials, doctors and survivors
The information on this website is proprietary and protected. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Any unauthorized or illegal use, copying or dissemination will be prosecuted. Please read our privacy policy and terms of service for more information about our website.
This website and its content may be deemed attorney advertising. Prior results do not predict a similar outcome.
The Mesothelioma Center’s claim as the most trusted resource is based on our more than 150 5-star Google and BBB reviews. Our organization also helps more than half of all mesothelioma patients annually diagnosed.
Your web browser is no longer supported by Microsoft. Update your browser for more security, speed and compatibility.
If you are looking for mesothelioma support, please contact our Patient Advocates at (855) 404-4592
The Mesothelioma Center at Asbestos.com has provided patients and their loved ones the most updated and reliable information on mesothelioma and asbestos exposure since 2006.
Our team of Patient Advocates includes a medical doctor, a registered nurse, health services administrators, veterans, VA-accredited Claims Agents, an oncology patient navigator and hospice care expert. Their combined expertise means we help any mesothelioma patient or loved one through every step of their cancer journey.
More than 30 contributors, including mesothelioma doctors, survivors, health care professionals and other experts, have peer-reviewed our website and written unique research-driven articles to ensure you get the highest-quality medical and health information.
My family has only the highest compliment for the assistance and support that we received from The Mesothelioma Center. This is a staff of compassionate and knowledgeable individuals who respect what your family is experiencing and who go the extra mile to make an unfortunate diagnosis less stressful. Information and assistance were provided by The Mesothelioma Center at no cost to our family.LashawnMesothelioma patient’s daughter


Asbestos.com. (2026, February 13). Mesothelioma Cells. Retrieved February 24, 2026, from https://www.asbestos.com/mesothelioma/cells/
"Mesothelioma Cells." Asbestos.com, 13 Feb 2026, https://www.asbestos.com/mesothelioma/cells/.
Asbestos.com. "Mesothelioma Cells." Last modified February 13, 2026. https://www.asbestos.com/mesothelioma/cells/.

Dr. Jacques Fontaine is a thoracic surgeon at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Florida, where he heads up the Mesothelioma Research and Treatment Center. He specializes in minimally invasive robotic surgery and aggressive surgeries for mesothelioma.
Our fact-checking process begins with a thorough review of all sources to ensure they are high quality. Then we cross-check the facts with original medical or scientific reports published by those sources, or we validate the facts with reputable news organizations, medical and scientific experts and other health experts. Each page includes all sources for full transparency.
Please read our editorial guidelines to learn more about our content creation and review process.
