Mesothelioma Diet & Nutrition
Diets for mesothelioma patients should avoid alcohol, processed meat, red meat and saturated fats. Mesothelioma patients should include more lean proteins in their diet such as poultry, fish, eggs, beans or peanut butter, incorporating them into each meal as possible.
Why Are Diet and Nutrition Important for Mesothelioma Patients?
Diet and nutrition can help strengthen the immune system to fight mesothelioma and infections. Certain foods can also help counter some of the effects of cancer. Consuming more proteins, for example, may help boost the immune system and restore tissue mesothelioma damages.
- Eat 5-6 small meals or snacks every 2 or 3 hours instead of 3 large meals daily.
- Choose nutrient-dense foods that are easy to eat. These can include full-fat Greek yogurt, eggs and salmon, whole milk, fruit and protein powder smoothies.
- If cooking smells bother you, avoid kitchens and try colder foods such as sandwiches.
- Experiment with different foods if you have taste changes to help you find more palatable ones.
- Try a mouthwash of 1 quart water, 3/4 teaspoon salt and 1 teaspoon baking soda to clear taste buds and relieve dry mouth.
- Eating at routine times can help keep your energy levels up and prevent malnutrition.
- Stay hydrated with water, milk, 100% fruit or vegetable juices and soups.
Nutrition also helps maintain energy levels. Consuming the right foods can give you the power to carry out daily activities. Before dietary changes are made, all patients should consult with their mesothelioma doctor.
Not only does what you eat matter when managing mesothelioma, but when you eat can also make a difference. Eating smaller portions throughout the day can help you get the nutrients you need without feeling too full or overwhelmed. If you’re not eating every 3 hours, set a timer. It’s easy to forget to eat when you’re not feeling well.
- Certain foods can reduce treatment side effects such as nausea or mouth sores.
- Eating the right foods provides energy to ease treatment-related fatigue.
- Proper diet and nutrition can help strengthen the immune system.
- Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce complications from treatment.

Get a free guide with the latest mesothelioma treatments and clinical trials.
Get Yours NowHow Does Nutrition Affect Mesothelioma Treatment?
A healthy, balanced diet can help patients respond better to treatment and reduce its side effects. For example, omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil may help reduce inflammation and improve heart health. This effect can benefit patients with a higher risk for heart problems.
Mesothelioma patients should consume a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins and minerals. Survivors may also be directed to limit whole grains or avoid other types of food during and while recovering from treatment.
A common diet concern for people with mesothelioma is eating too few calories, which are essential to aid recovery, support immunity and fight fatigue. It’s important to keep your energy levels up and give your body the nutrients it needs to heal.
Understanding Nutrition During Mesothelioma Treatment
Mesothelioma treatment can affect your ability to eat as you usually do. Alterations to your diet and eating habits can help you cope with treatment and its side effects. Taking proactive measures to meet nutritional needs for each type of treatment can help.
- Chemotherapy: Liquid or soft foods can reduce chewing if mouth sores develop. Avoiding icy or frozen foods can help with cisplatin-induced cold sensitivity. Chemotherapy can change how food tastes. Eating with plastic utensils can help if food tastes metallic.
- Immunotherapy: Toast, oatmeal, broth and baked or broiled proteins such as chicken or tofu are often recommended for patients experiencing immunotherapy side effects such as nausea. Side effects require immediate attention from your oncologist.
- Pain Medications: Certain pain medications can decrease appetite, cause nausea and contribute to constipation. Increasing dietary fiber and water can help lessen constipation. Always drink plenty of water when increasing fiber. Without adequate fluids, constipation may worsen.
- Radiation Therapy: Receiving radiation therapy around the chest can impact swallowing. While rare for peritoneal mesothelioma patients to receive radiation around the abdomen, this can cause digestive issues such as nausea, vomiting, cramps, bloating and diarrhea.
- Surgery: Some people may need to gain weight before surgery. A healthy weight before mesothelioma surgery can improve wound healing, reduce infection risk and aid recovery. Proper nutrition after your surgery will also replace blood loss and increase your energy level.
Some aspects of treatment may affect how you get nutrition. For example, abdominal surgeries can complicate eating and digestion. Some peritoneal mesothelioma patients may receive nutrition intravenously shortly after abdominal surgery.

More than 95% of my mesothelioma patients talk to me about losing weight. We get nutrition involved before we start our multimodality treatment program. We assess how much protein and how many calories they need. To get treatment, you have to have some type of nutrition program involved.
Foods to Aid Recovery After Mesothelioma Treatment
Some foods contain nutrients that may support recovery after mesothelioma treatment. Speak with your doctor about which foods or nutrients they recommend you add to your current diet.
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Vegetables, fruit, beans, potatoes and nuts can balance insulin levels, possibly minimizing cancer cell growth.
- Green Tea: This tea is rich in antioxidants.
- Medicinal Teas: Essiac tea or moringa leaf are antioxidant-rich and may have limited anti-cancer actions in the body, though more research is needed to assess potential benefits.
- Natural Sources of Coenzyme Q: The nutrient in beef, chicken, pork, trout, herring, sardines, soybeans, lentils and peanuts may protect the heart from chemo damage.
- Omega-3 Fats in Fish: May reduce harmful weight loss and inhibit metastasis.
- Other Herbal Teas: Chamomile, ginger, mint and hibiscus may have anti-cancer properties.
- Spices: Turmeric, basil, oregano, rosemary, mint, dill and others may have anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory benefits.
While antioxidants are generally considered part of a healthy diet, they neutralize free radicals. Many chemotherapy drugs use free radicals to attack cancer cells. Chemotherapy patients may be advised to avoid foods high in antioxidants. Speak to your doctor about possible interactions.
Foods to Avoid During and After Mesothelioma Treatment
Patients may want to avoid certain foods or nutrients that could worsen side effects or weaken the immune system. Foods that are difficult to digest can exacerbate mesothelioma-related or treatment-related digestive problems.
- Alcohol: Limiting or eliminating alcohol consumption is advisable as it can harm cells and DNA, possibly interfering with medications.
- Certain Meats: Processed meats, such as cured bacon, sausage and hot dogs, can contribute to inflammation.
- Irritating Foods: Acidic, sour and spicy foods can irritate chemotherapy-related mouth sores.
- Salty Foods: Snacks high in sodium lead to fluid retention that may worsen shortness of breath.
- Sugary Foods: Sweets are often low in nutrients. Excess sugar may contribute to inflammation and reduced immune function.
Some foods, such as grapefruits, can negatively interact with chemotherapy and other mesothelioma drugs. Your doctor will tell you about specific foods that may interact with your medications.
Dietary Supplements for Mesothelioma Patients
Before taking any dietary supplements, it’s important to note that nutritional and herbal supplements usually are less well-researched than mainstream medications. This makes it even harder to predict what problems they may cause when combined with chemotherapy.
Discuss any supplements you’re considering with your mesothelioma care team before taking them. They can provide guidance on which supplements are safe to take. They’ll also tell you which ones to avoid during mesothelioma treatment.
- Amino acids
- Beta-carotene
- Minerals like calcium, magnesium, selenium and zinc
- Protein supplements
- Vitamins A, B9 (folic acid), B12, D and E
Dietary supplements can interact with cancer drugs. These interactions may make them less effective or cause harmful side effects. High levels of vitamin C or E can interfere with radiotherapy. St. John’s wort, ginseng and garlic supplements may also interfere with chemo drugs.
Even traditional supplements doctors may recommend can have harmful interactions with mesothelioma therapy. Mesothelioma patients on chemotherapy are often prescribed folic acid and B12 supplements to reduce toxic side effects but, vitamin B6 supplements can interact negatively with cisplatin.

Ease your mesothelioma symptoms with the right food. See recipes designed for you.
Get My Free GuideMeal Planning for Your Mesothelioma Diet
Meal planning can alleviate the stress associated with food shopping. Meal prepping will also make crafting and following your mesothelioma diet easier.
As a caregiver, stock up on the patient’s favorite foods when food shopping. Buy items essential for meeting their nutritional needs. This can reduce the need to shop often.
Planning Healthy Portions
The U.S. Department of Agriculture retired the Food Guide Pyramid years ago and replaced it with My Plate. However, My Plate isn’t designed to give people with cancer information about their specific nutrition needs before, during and after treatment.
The Harvard School of Public Health created the Healthy Eating Plate. It’s a better starting place for designing a healthy diet for people with mesothelioma.
The effects of cancer and treatment can make it challenging to eat. Mesothelioma patients also have specific nutritional needs. You’ll need to adjust the Healthy Eating Plate guidelines during cancer therapy to find the best mesothelioma diet for you.
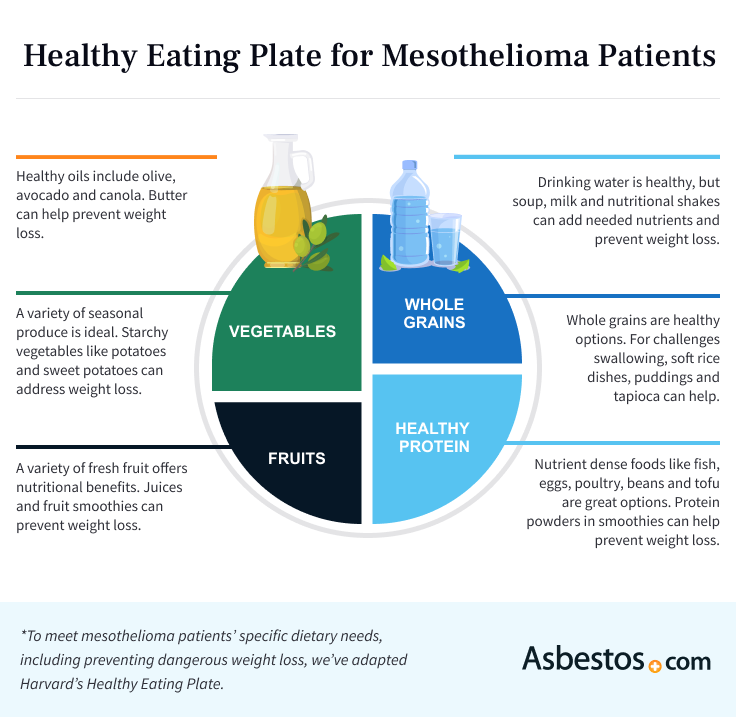
Replace green vegetables, salads and other lower-calorie foods with starchy vegetables such as potatoes and sweet potatoes. For most mesothelioma patients, it’s helpful to increase the protein portion of the plate and decrease whole grains a bit. Sometimes, you may need to add a high-protein, high-calorie liquid nutrition supplement.
Tips to Get More from Your Meals
Eating enough and getting proper nutrition can be challenging if you have mesothelioma. Patients may have difficulty eating and require additional nutrients to maintain their weight and strength.
- Eat multiple small meals throughout the day instead of 3 large ones.
- Snack whenever you’re hungry, even if it is not mealtime. Enjoy the foods that appeal to you at the time.
- Drink liquids after meals or as snacks, not before or during mealtime. Liquid can fill you up before you have the chance to consume the whole, nutrient-dense foods on your plate.
- Include a portion of protein such as poultry, fish, eggs, beans or peanut butter at each meal.
- You may consume your favorite foods any time of day. If you love breakfast foods, eating them for lunch or dinner is OK.
- Juice fresh fruits and vegetables to obtain their nutrients without filling up.
If you don’t own a juicer, you can create a juice with a blender and cheesecloth. Blend fruit or vegetables with filtered water, then strain with a cheesecloth available at most grocery stores.
Try to create a joyful or relaxing setting, enjoying food with friends or family. This may reduce stress around eating and lead to more enjoyment while consuming the foods you need.
Tips for Adding More Protein to Your Diet
Mesothelioma patients may struggle to maintain their muscle mass and strength. Eating protein-rich foods regularly is an important part of keeping muscle and fighting fatigue.
Protein examples include chicken, fish, lean beef and pork, Greek yogurt, beans, nuts, spinach, cheese, eggs and soy foods such as tofu or tempeh. Try to eat more of these foods if you’ve lost weight or strength.
- Add cheese to omelets, sandwiches, soups, salads and casseroles.
- Powdered milk can be added to milk, milkshakes, cream-based soups and mashed potatoes.
- Add cooked meats to omelets, soups and salads.
- Blend nut butter and protein powder into smoothies and milkshakes.
Snacks between meals can include protein like cheese, nut butter, roasted nuts or sliced meats. Desserts made with eggs such as cheesecake, custard and pudding can increase protein consumption.
Tips for Adding More Calories to Meals
Mesothelioma patients often struggle with maintaining a healthy weight as a result of treatment-related side effects. Adding extra calories to meals can be challenging, but patients must get the necessary nutrients to help their bodies fight cancer.
- Avoid foods labeled as low-fat, nonfat and low-calorie.
- Drink high-calorie beverages like milkshakes with added ice cream or fruit nectars.
- Cook with butter and oil and add them to meals when possible, including high-calorie dressings.
- Add avocado to sandwiches and salads. Eat guacamole with tortilla chips.
- Smear cream cheese onto bagels, sandwiches or crackers.
- Top vegetables with creamy or cheesy sauces.
- Add Greek yogurt, heavy cream or sour cream to dessert recipes, sauces and soups.
These tips may help those who are losing weight to maintain their current weight. Maintaining weight and muscle mass is important for those undergoing cancer treatment. It helps the body handle the aggressive nature of anticancer therapies.
Prepare meals in advance and freeze them into meal-sized portions that are easy to heat. Talk with a dietitian if you want assistance planning your meals or preparing a grocery list.
Food Safety and Mesothelioma
For people undergoing mesothelioma treatment, food safety is crucial. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services outlines four critical steps to ensure food safety: clean, separate, cook and chill.
- Clean: When cleaning foods, avoid using soap, detergents and commercial produce rinses. Instead, rinse fruits and vegetables under running water. Make sure to wash your hands with warm, soapy water before and after touching food.
- Separate: To prevent cross-contamination, always use a clean knife when cutting different foods, particularly raw meats. Clean countertops and cutting boards using hot, soapy water or wipes designed for use around food. Keep raw meat in the refrigerator or freezer, sealed and separated from other food.
- Cook: Proper cooking and cooling of foods are essential. Cook meats to the appropriate temperature to avoid consuming raw or undercooked meat. Keep hot foods hot (above 140°F) and cold foods cold (below 40°F).
- Chill: Perishable foods should be quickly refrigerated or frozen. Defrosted food should be used immediately without refreezing.
Cancer therapies like radiation and chemotherapy often weaken the immune system. A weakened immune system may not correctly fight bacteria, parasites or other potentially dangerous organisms in food.
Avoiding Food-Borne Illnesses
Foodborne illnesses or “food poisoning” can cause serious adverse effects. Mesothelioma patients should avoid raw or undercooked meat, poultry, seafood and eggs to avoid feeling sick from food. Unpasteurized or raw milk and cheeses should also be avoided.
Food Poisoning Side Effects
- Abdominal cramps
- Dehydration
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Fever
- Flu-like illness
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle aches
- Nausea
- Upset stomach
- Vomiting
- Weakness
Paying attention to reports of food recalls and food-related disease outbreaks can also help prevent health complications. Avoid any contact with or consumption of suspected foods.
For example, the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service issued a public health alert in December 2022 for ground beef that tested positive for E. coli. That same month, the Kraft Heinz Company recalled approximately 2,400 pounds of ready-to-eat ham and cheese loaf because of possible cross-contamination with under-processed products.
Common Questions About Nutrition & Mesothelioma
- What is the best diet for mesothelioma patients?
-
Mesothelioma doctors recommend that cancer patients eat foods rich in nutrients such as eggs, fruit and salmon. Also, patients should have a diet high in protein with starchy vegetables and plenty of water to counter the effects of mesothelioma treatment.
- Can a registered dietician help me develop a personalized nutrition plan?
-
A registered dietitian can assess your nutritional needs and help develop a personalized nutrition plan. They’ll base a program on your needs, preferences and health status, including mesothelioma. A registered dietitian can also help you navigate any dietary restrictions or challenges that may arise during your treatment.
- Can certain foods or drinks interfere with my medications or treatments?
-
Yes, some foods may interact with chemotherapy drugs, which can impact their effectiveness or cause side effects. Supplements may also interfere with cancer treatments. A registered dietitian can guide you on potential interactions. Discuss any supplements or dietary changes with your health care team.
- How do you cure mesothelioma with diet?
-
While no mesothelioma cure exists, a healthy diet can offset the adverse effects of cancer therapy and improve the treatment outcome. Eating the right foods can make treatment recovery more manageable and improve prognosis.
- What diet helps prevent mesothelioma?
-
A healthy diet and exercise are essential for lowering mesothelioma risks and other cancers. A healthy eating pattern will control your weight through various fruits, vegetables, fiber sources and low-calorie foods. Limiting your intake of red meats, sugar-sweetened beverages and highly processed foods will also lower your risk of cancer.
- Does mesothelioma cause weight loss?
-
Unexplained weight loss is one of the signs of advanced mesothelioma. Weight loss can also be due to a lack of appetite or persistent nausea, which are symptoms of peritoneal mesothelioma.






