
Connect with top-rated doctors specializing in mesothelioma treatment, who will personalize treatment options based on your diagnosis.
Find Your DoctorCTLA-4 is a protein on immune cells that slows the immune response. Mesothelioma cells use CTLA-4 to avoid immune detection. CTLA-4 inhibitor drugs like Yervoy (ipilimumab) and Imjudo (tremelimumab) block this protein, helping immune cells find and fight cancer more effectively.
CTLA-4, officially named cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4, is a protein found on the surface of T cells involved in mesothelioma. These cells help the immune system fight off viruses, bacterial infections and cancers like mesothelioma. CTLA-4 acts like a brake, stopping the immune system from attacking healthy cells.
Mesothelioma cells can take advantage of these brakes to hide from the immune system. Blocking CTLA-4 helps release the “brakes,” making it easier for immune cells to find and attack mesothelioma. Because CTLA-4 acts as a brake, it’s called an immune checkpoint protein. Drugs that block CTLA-4 are called immune checkpoint inhibitors.
These drugs help the immune system find and fight cancer, which may help people with mesothelioma live longer. Targeting CTLA-4 with checkpoint inhibitors is a form of immunotherapy. New immunotherapy treatments offer some of the most promising options for mesothelioma today.
Yervoy (ipilimumab) is a common CTLA-4 inhibitor drug used to help the immune system fight mesothelioma. It’s FDA-approved only as a first treatment when combined with Opdivo (nivolumab). Yervoy is also a type of medicine called a monoclonal antibody, which is a lab-made protein that works like your body’s natural antibodies. Doctors usually give Yervoy every 6 weeks and Opdivo every 3 weeks.
Researchers are also testing new CTLA-4 drugs for mesothelioma. Imjudo (tremelimumab) is a CTLA-4 inhibitor usually paired with Imfinzi (durvalumab) in clinical trials, but it’s not yet FDA-approved for mesothelioma. Researchers are also studying new drugs like Cadonilimab (AK104), which targets both CTLA-4 and PD-1 (another checkpoint protein). Erfonrilimab, which targets CTLA-4 and PD-L1 (another checkpoint protein), is also being studied as a mesothelioma treatment.
Mesothelioma uses CTLA-4’s natural role as an immune system brake to protect itself from attack. Normally, CTLA-4 helps prevent T cells from overreacting and damaging healthy tissue. But mesothelioma tumors take advantage of this system, increasing CTLA-4 activity, which keeps T cells from recognizing and destroying cancer cells. This allows the tumor to hide from the immune system and continue to grow.
A recent study published in the Chinese Journal of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Diseases found people with higher levels of CTLA-4 may have shorter survival times from mesothelioma. This is especially true in cases of pleural mesothelioma, the most common type of this cancer.
That’s why drugs that block CTLA-4 are so important in mesothelioma treatment. In addition to boosting T cell activity, CTLA-4 inhibitors can also increase the number of T cells that enter the tumor and help trigger a broader immune response. This deeper immune activation is one reason why checkpoint inhibitors like Yervoy and Keytruda (pembrolizumab), which blocks the PD-1 protein, are a key part of new mesothelioma therapies.
Pastor and mesothelioma survivor Dr. Berlinda Love has begun treatment with CTLA-4 inhibitor Yervoy paired with Opdivo. She tells us her tumor has shrunk since beginning her immunotherapy regimen. “When we started out it was about 10 ten centimeters,” she shares. “The doctors were really impressed. It had shrunk down to about 5 centimeters.”
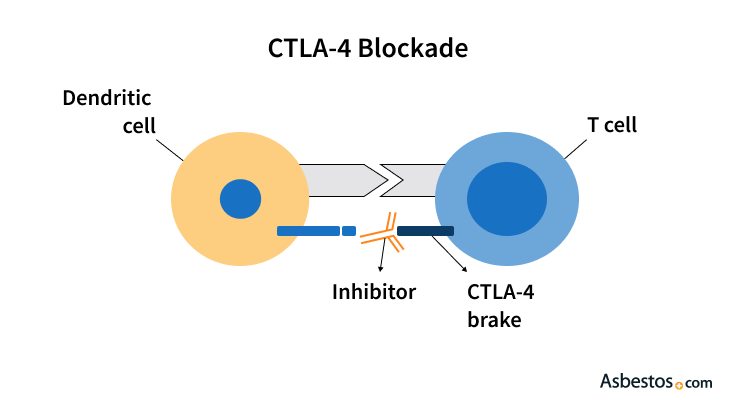
Yervoy and Imjudo are usually combined with other drugs that target different checkpoint proteins to boost the immune system’s ability to fight mesothelioma. Yervoy is usually paired with Opdivo, which targets the PD-1 protein. Imjudo is usually paired with Imfinzi, which targets the PD-L1 protein. Active clinical trials for mesothelioma are looking at other pairing possibilities as well.
Research is key to finding better treatments for mesothelioma. For example, at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting, French researchers reported about 44% of mesothelioma patients had their cancer controlled with Opdivo alone. When Yervoy was added, that number increased to 50%. These encouraging results led to a larger clinical trial, and eventually, the FDA approval of the Yervoy and Opdivo combination for treating mesothelioma.
Mesothelioma Studies Featuring Imjudo (Tremelimumab)
Scientists continue to study CTLA-4 drugs like Yervoy and Imjudo with different drugs. They’re also being studied in combination with chemotherapy. Speak to your doctor or a Patient Advocate about clinical trials of CTLA-4 inhibitors you may be able to participate in.

Connect with top-rated doctors specializing in mesothelioma treatment, who will personalize treatment options based on your diagnosis.
Find Your DoctorWhen people with mesothelioma take CTLA-4 inhibitors, their immune system becomes more active, which can lead to side effects. These happen because the immune system may attack healthy tissues, not just cancer cells. Side effects from CTLA-4 inhibitors are usually different from those seen with chemo.
Common Side Effects of CTLA-4 Inhibitors
Unlike chemo, which often causes nausea, hair loss and low blood counts, CTLA-4 inhibitors mainly cause side effects related to the immune system being overactive. Some side effects can be serious if they’re not treated quickly. It’s important to tell your doctor right away if you notice any new or worsening symptoms during treatment
A major difference between chemo and immunotherapy is symptom severity. Peritoneal mesothelioma survivor Randy Derouen tells us chemo gradually wore him down, “The good thing about immunotherapy is it doesn’t linger. I’d be fatigued with chemotherapy for 10 or 11 days.”
CTLA-4 and PD-1 inhibitors both help the immune system fight mesothelioma, but they work at different stages. CTLA-4 inhibitors help T cells, removing early “brakes” on the immune system. PD-1 inhibitors help T cells keep fighting at the tumor site, blocking signals cancer uses to shut them down. Doctors may use both drugs together to boost the immune response against mesothelioma.
CTLA-4 inhibitors can’t cure mesothelioma, but they can slow the cancer down to help some people live longer. These drugs help the immune system attack cancer cells and sometimes shrink tumors. Doctors often combine them with other mesothelioma treatments for better results. Researchers are still learning who benefits the most from CTLA-4 inhibitors.
CTLA-4 inhibitors are generally safe for many people, but they can cause serious side effects, especially with long-term use. These side effects happen when the immune system attacks healthy parts of the body. You may need to stop treatment or take steroids to manage symptoms. Inform your doctor about any side effects.
Stay up-to-date on treatment, research, clinical trials, doctors and survivors
The information on this website is proprietary and protected. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Any unauthorized or illegal use, copying or dissemination will be prosecuted. Please read our privacy policy and terms of service for more information about our website.
This website and its content may be deemed attorney advertising. Prior results do not predict a similar outcome.
The Mesothelioma Center’s claim as the most trusted resource is based on our more than 150 5-star Google and BBB reviews. Our organization also helps more than half of all mesothelioma patients annually diagnosed.
Your web browser is no longer supported by Microsoft. Update your browser for more security, speed and compatibility.
If you are looking for mesothelioma support, please contact our Patient Advocates at (855) 404-4592
The Mesothelioma Center at Asbestos.com has provided patients and their loved ones the most updated and reliable information on mesothelioma and asbestos exposure since 2006.
Our team of Patient Advocates includes a medical doctor, a registered nurse, health services administrators, veterans, VA-accredited Claims Agents, an oncology patient navigator and hospice care expert. Their combined expertise means we help any mesothelioma patient or loved one through every step of their cancer journey.
More than 30 contributors, including mesothelioma doctors, survivors, health care professionals and other experts, have peer-reviewed our website and written unique research-driven articles to ensure you get the highest-quality medical and health information.
My family has only the highest compliment for the assistance and support that we received from The Mesothelioma Center. This is a staff of compassionate and knowledgeable individuals who respect what your family is experiencing and who go the extra mile to make an unfortunate diagnosis less stressful. Information and assistance were provided by The Mesothelioma Center at no cost to our family.LashawnMesothelioma patient’s daughter


Selby, K. (2026, February 9). CTLA-4 and Mesothelioma. Asbestos.com. Retrieved February 27, 2026, from https://www.asbestos.com/treatment/immunotherapy/ctla4/
Selby, Karen. "CTLA-4 and Mesothelioma." Asbestos.com, 9 Feb 2026, https://www.asbestos.com/treatment/immunotherapy/ctla4/.
Selby, Karen. "CTLA-4 and Mesothelioma." Asbestos.com. Last modified February 9, 2026. https://www.asbestos.com/treatment/immunotherapy/ctla4/.

Dr. Andrea Wolf is the Director of the New York Mesothelioma Program at Mount Sinai in New York City. She focuses on multidisciplinary treatment, clinical research, community outreach and education.
Our fact-checking process begins with a thorough review of all sources to ensure they are high quality. Then we cross-check the facts with original medical or scientific reports published by those sources, or we validate the facts with reputable news organizations, medical and scientific experts and other health experts. Each page includes all sources for full transparency.
Please read our editorial guidelines to learn more about our content creation and review process.
