“20-Year Peritoneal Mesothelioma Survivor Celebrates Life Tammy Frank was diagnosed with peritoneal mesothelioma in 1999. After undergoing surgery, radiation and chemo, she has become a 20+ year survivor. Tammy credits her longevity to early treatment and a deep sense of purpose.
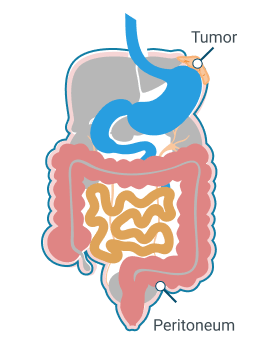
Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Peritoneal mesothelioma is the second most common type of this cancer, accounting for 10%-30% of all cases. Irritation from asbestos exposure can cause mesothelioma tumors to grow in the abdominal lining. Surgery and heated chemotherapy can improve outcomes and relieve symptoms.
What Is Peritoneal Mesothelioma?
Peritoneal mesothelioma is a rare asbestos-related cancer that forms in the peritoneum. The peritoneum is the thin tissue lining the cavity and organs in your belly. This type of cancer is also called abdominal mesothelioma.
Access top mesothelioma doctors, and get help scheduling appointments.
Find a Top DoctorKey Facts About Peritoneal Mesothelioma
- Peritoneal mesothelioma accounts for 10% to 30% of all cases, with approximately 300 to 900 new cases diagnosed annually.
- About 65% of patients with peritoneal mesothelioma live for 5 years or more.
- The average life expectancy without any treatment is 6 months.
The most common symptoms of peritoneal mesothelioma are stomach pain, swelling, digestive problems and weight loss. Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy or immunotherapy to help control the disease and improve quality of life.
What Are the Symptoms of Peritoneal Mesothelioma?
Common symptoms of peritoneal mesothelioma include abdominal pain, bloating and fluid buildup. Fluid in the belly puts pressure on internal organs causing pain and discomfort.
Epifanio Figueroa tells us his first sign of peritoneal mesothelioma was abdominal swelling. He shares, “It started with my stomach growing and it didn’t stop getting bigger. It was liquid that was being accumulated. It was from mesothelioma, but we didn’t know that at the time.”
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Symptoms
Other signs of mesothelioma are changes in bowel movements, weight loss or fever. Most symptoms appear in later stages of the disease. A 2023 report in Radiology Case Reports also discussed the risk of bowel obstruction with peritoneal mesothelioma. Early stage mesothelioma affects the digestive system, including changes in bowel habits.
Late stage mesothelioma usually includes significant abdominal pain, fluid buildup, weight loss, fatigue, nausea, vomiting and bowel obstruction. Rare and severe symptoms include, blood clots and fluid buildup in other places such as around the lungs (pleural effusion) or sac around the heart (pericardial effusion).
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Symptoms by Demographics
Peritoneal mesothelioma symptoms can look different for each person. Things like age, gender and race can affect when and how symptoms show up. Younger people may not notice signs right away because the disease often takes many years to develop.
Men and women sometimes experience different symptom patterns. Studies indicate some racial groups may experience different symptom patterns as well.
| Symptom | Percentage of Males | Percentage of Females |
|---|---|---|
| Abdominal Pain | 68% | 74% |
| Fatigue | 75% | 80% |
| Weakness | 62% | 66% |
| Loss of appetite | 54% | 60% |
| Unexplained weight loss | 60% | 65% |
| Bowel obstruction | 38% | 42% |
| Fever | 27% | 33% |
Causes of Peritoneal Mesothelioma
The main cause of peritoneal mesothelioma is breathing in or swallowing asbestos fibers. These tiny fibers can travel into the belly and get stuck in the peritoneum. After a long time, they can cause irritation and damage that may lead to cancer. This slow process is called the latency period, and it can take many years to happen.
If you have a history of asbestos exposure, let your doctor know. You could be at a higher risk of developing peritoneal or pleural mesothelioma, which develops in the lining of the lungs and is the most common type of mesothelioma. Your doctor may recommend regular mesothelioma screenings for you.
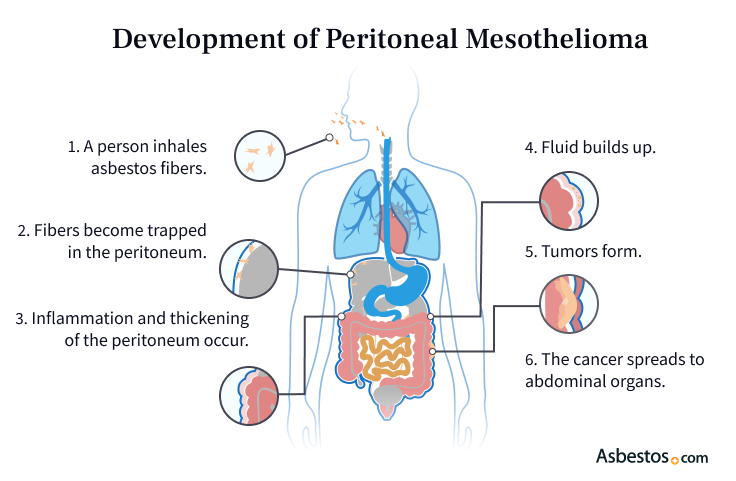
Risk Factors for Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Exposure to asbestos is the largest risk factor for peritoneal mesothelioma. Most people are exposed at work.
Duration of the exposure plays a key role in the likelihood of the disease developing. There is no safe level of asbestos exposure. Even short-term exposure isn’t safe.
Common Risk Factors for Peritoneal Mesothelioma
- Age
- Duration of asbestos exposure
- Exposure to radiation
- Family history
- Gender
- Genetics
- Occupation
Family members of asbestos workers are also at a higher risk of exposure. Occupational exposure can lead to secondary exposure. Workers can take asbestos fibers home on their clothes, hair or skin. Doing laundry, hugging a loved one in their work clothes and touching contaminated gear can lead to secondary exposure.
We spoke to mesothelioma survivor James D. about his peritoneal mesothelioma. He told us the exposure happened while working as a mechanic in Chicago. Many survivors also tell us they were exposed to asbestos while serving in the U.S. Armed Forces.

Discover how mesothelioma doctors personalize treatment plans for you.
Sign up nowHow Is Peritoneal Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
A biopsy or tissue sample is the only way to confirm a peritoneal mesothelioma diagnosis. The diagnostic process usually begins with a physical exam where your doctor will feel for any abnormalities in your belly. Imaging tests like X-rays and blood tests may then be ordered.
Dr. Anton Strocel, who treated Trina Reif, a 20-year survivor of peritoneal mesothelioma, tells us, “She presented to me with unexplained ascites.” Ascites is the buildup of excess fluid in the belly. Trina then had an exploratory laparotomy and peritoneal biopsies before her diagnosis was confirmed.
Diagnostic Tests for Peritoneal Mesothelioma
- Biopsy: A small sample of your tissue or fluid is collected to check for cancer cells.
- Blood tests: Samples of your blood are studied for signs, called “biomarkers,” of specific diseases. For example, mesothelin, fibulin-3 and CA125 are proteins often found in higher amounts in people with mesothelioma.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRIs or PET scans can show if there are abnormalities or mesothelioma tumors and help determine how far they’ve spread in your body.
A small sample of tissue from your biopsy is sent to a pathologist. The pathologist will then look at the tissue under a microscope to see if mesothelioma cells are present and to confirm your mesothelioma diagnosis. The specific type of mesothelioma cells found will also be included in your pathology report. Mesothelioma cells include: epithelioid, sarcomatoid or biphasic (a mix of both). Each cell type grows and spreads differently, so knowing this helps your doctor choose treatments most likely to work best for you.
Finding peritoneal mesothelioma early is important but often hard. Symptoms can take 20 to 60 years after exposure to appear and when they do, they can look like signs of other common illnesses.
Staging Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Peritoneal mesothelioma staging shows how far the disease has spread. The Peritoneal Cancer Index is the system most used to stage peritoneal mesothelioma. PCI measures the size and spread of tumors in the abdomen. This information can help determine treatment options.
In stage 1, or early-stage peritoneal mesothelioma, the cancerous tissue is small. Tumors are only within the abdominal lining and lymph nodes are free of cancer. In stage 2, or mid-stage peritoneal mesothelioma, cancerous tissue is moderate. Tumors haven’t spread outside the lining or into lymph nodes. During stage 3 and stage 4, or late-stage mesothelioma, the cancerous tissue spreads more widely.
Treatments for Peritoneal Mesothelioma
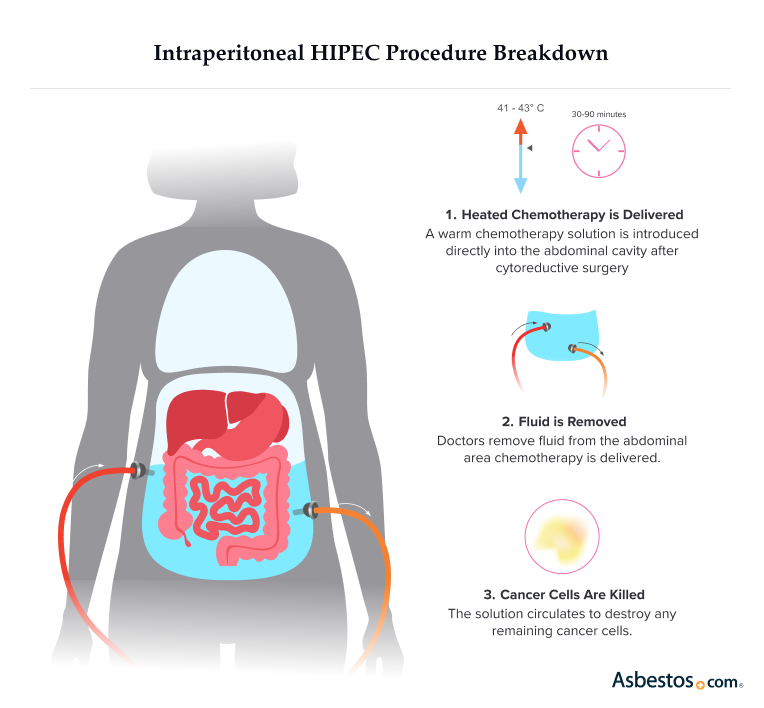
Your doctor might suggest a mesothelioma treatment plan that combines several therapies. For peritoneal mesothelioma, this may include heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy. This is a warm chemo wash after surgery as part of a 2-step procedure to remove and kill cancer cells. HIPEC is considered a gold-standard treatment for peritoneal mesothelioma.
Common Peritoneal Mesothelioma Treatments
- Chemotherapy: Chemo drugs target peritoneal mesothelioma cells. They enter these cells, kill them and stop their spread. This is the most common treatment for peritoneal mesothelioma.
- HIPEC: Heated chemo drugs are applied directly to the abdomen during surgery. Doctors infuse and circulate the drugs throughout the peritoneal cavity to treat any remaining cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Drugs are used in immunotherapy for peritoneal mesothelioma that boosts the immune system to find and fight cancer cells. Immunotherapy boosts how the body fights the disease.
- Palliative care: This includes treatments such as chemo, immunotherapy and surgery. These options help manage pain and other symptoms. They also aim to improve a patient’s quality of life. This can happen at any point alongside other treatments.
- Radiation: This uses high-energy particles or X-rays to kill cancer cells. This can be given with chemo or immunotherapy. It helps improve survival and relieve symptoms of peritoneal mesothelioma.
- Surgery: Peritonectomy is a procedure that removes the peritoneal lining as part of tumor-removing or cytoreductive surgery. An omentectomy can also be done during cytoreductive surgery and removes the omentum, a fold of tissue that’s part of the peritoneum.
- Targeted therapy: These treatments focus on specific genetic changes in cancer cells.
Dr. Joseph Skitzki, a surgical oncologist at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, regularly performs HIPEC for his peritoneal mesothelioma patients. He tells us, “The results are quite impressive. About 80% of patients who are eligible for the treatment will be alive at 5 years, and about half of that number without any further evidence of disease.”
If surgery isn’t an option, your doctor may recommend immunotherapy or targeted therapy. You may also choose to participate in a clinical trial to try new treatments or approaches. Your doctor and Patient Advocates can help share more information about trials that are actively looking for people to participate and could be helpful for you.
Finding a Peritoneal Mesothelioma Specialist
It’s important to find the right mesothelioma specialist to treat peritoneal mesothelioma. These specialists understand the unique challenges of this rare cancer. Your regular doctor can help you find one. Our team of Patient Advocates can also connect you with the right specialist and cancer center.
Choosing a top mesothelioma treatment center can help you get better results. These centers often offer clinical trials and provide support for you and your family. You may have the chance to join a study that tests new treatments for mesothelioma. Researchers use what they learn to improve care and find better ways to prevent the disease.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Life Expectancy & Survival Rate
The average life expectancy for peritoneal mesothelioma is about 31 months after diagnosis. Treatment options and prompt treatment can affect your prognosis. Early detection and HIPEC surgery boost survival rates.
Aggressive treatments such as surgery help about 50% of patients live 5 years or more. Patients without treatment have a life expectancy of 6 to 8 months. Adopting healthy habits and new treatments may extend life expectancy.
Peritoneal Survival Rates
- About 75% of patients who have surgery and then chemo live longer than 5 years.
- More than 50% of peritoneal cancer patients who had HIPEC surgery live more than 5 years.
- The overall 5-year survival rate is 65%, but the average life expectancy of peritoneal mesothelioma without treatment is 6 months.
- People who don’t qualify for surgery live about 13 months with chemo alone.
Age, gender, genetics, the stage of mesothelioma, cell type and tumor location can affect your prognosis. Women usually have a better outlook than men for peritoneal mesothelioma. People with the epithelioid cell type also typically have a better prognosis as it responds better to treatment. Your prognosis also improves if all tumors are able to be completely removed.

Access trust funds and grants to ease the cost of your treatment.
Get Help NowLiving With Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Living with peritoneal mesothelioma can be tough. However, a solid support system of family, friends and health care providers makes a big difference. Both patients and caregivers may face physical and emotional issues. Rest, proper nutrition and gentle movement can help you feel your best.
Collaborating with your medical team helps you get the right care. This support is key for managing symptoms and enjoying a better quality of life. Meeting and talking to others who are on a similar journey as yourself can also help. Joining a support group is a great way to find relief when dealing with hurdles of your diagnosis.
- Updated 2025 ASCO guidelines for treating peritoneal mesothelioma recommend using a combination of chemotherapy drugs gemcitabine with either cisplatin or carboplatin.
- Newer peritoneal mesothelioma treatment guidelines also show the diagnostic process should include a CT of the chest with contrast plus a CT or MRI of the abdomen or pelvis with contrast.
“The best treatment for peritoneal mesothelioma is a combination of HIPEC and pressurized intraperitoneal aerosolized chemotherapy, also known as PIPAC, which differs from traditional chemo because it uses pressure to turn the chemo drugs into a mist to reach the abdominal area better.”
Common Questions Our Patient Advocates Are Asked
- Is there a cure for peritoneal mesothelioma?
-
There is no cure for malignant peritoneal mesothelioma. But it can go into remission. About 12% of peritoneal mesothelioma patients who get aggressive treatment have complete remission. Partial remission is also possible. Remission isn’t the same as a cure. Doctors watch patients closely. Cancer can return after remission.
- Can peritoneal mesothelioma go into remission?
-
Yes, it can go into remission. About 12% of peritoneal mesothelioma patients who get aggressive treatment have complete remission. Partial remission is also possible. Remission isn’t the same as a cure. Doctors watch patients closely. Cancer can return after remission.
- Any tips for managing a peritoneal mesothelioma diagnosis?
-
Managing a cancer diagnosis is challenging for patients and their loved ones. There is no one right way to cope with mesothelioma. Knowing the details of your diagnosis can help you decide. Talking to a counselor, joining a support group, and eating well are all helpful. So are relaxing and exercising to manage your mental health.
Compensation for peritoneal mesothelioma can help pay for treatment. Legal options include lawsuits, settlements and trust funds.
- What questions should I ask my doctor about peritoneal mesothelioma?
-
Effective communication with your doctor is key. Here’s a short list of questions to ask.
- Has my cancer spread beyond my abdomen?
- What are my treatment options?
- How can I manage side effects and symptoms?
- Do I qualify for surgery or HIPEC?
- How can I access emerging treatments or clinical trials?
Prepare questions before medical appointments. It’ll help you communicate with care providers. You will also have more control over your diagnosis and treatment.
- Can peritoneal mesothelioma be misdiagnosed?
-
Peritoneal mesothelioma is often misdiagnosed. It happens because of its non-specific symptoms. Many patients are first
Peritoneal mesothelioma is often misdiagnosed. It happens because of its non-specific symptoms. Many patients are first diagnosed with IBS, ovarian cancer or other gut issues. Later, they receive an accurate mesothelioma diagnosis.