Isabel De La Camara was diagnosed with peritoneal mesothelioma in 2008. She believes the disease traces back 3 decades ago when she worked at a factory in Puerto Rico. Despite her diagnosis, Isabel is determined to remain joyful and live life to the fullest.
Mesothelioma Symptoms & Signs
Mesothelioma symptoms depend on the location and stage of the cancer. Common symptoms of pleural mesothelioma are chest pain, shortness of breath and weight loss. Peritoneal mesothelioma often causes fluid buildup, abdominal pain and swelling. Early mesothelioma detection can improve survival.
What Are the Symptoms of Mesothelioma?
Common symptoms of mesothelioma include pain, loss of appetite, fever and excessive sweating. Symptoms will vary depending on where the cancer starts and its stage. Fatigue, weakness and unexplained weight loss can also be signs of mesothelioma.
Mesothelioma may not cause symptoms until it is more advanced. The more advanced the cancer, the more likely the tumor has grown to affect the surrounding organs. Early signs of mesothelioma include chest or abdominal pain, coughing or wheezing and fatigue. Late-stage mesothelioma symptoms include bowel obstruction, difficulty swallowing and trouble breathing.
Access top mesothelioma doctors, and get help scheduling appointments.
Find a Top DoctorCommon signs of mesothelioma may also be symptoms of other diseases, so diagnosing it can be challenging. If you are experiencing mesothelioma symptoms or have a history of asbestos exposure, consult a specialist. Early diagnosis is key to a favorable outcome.
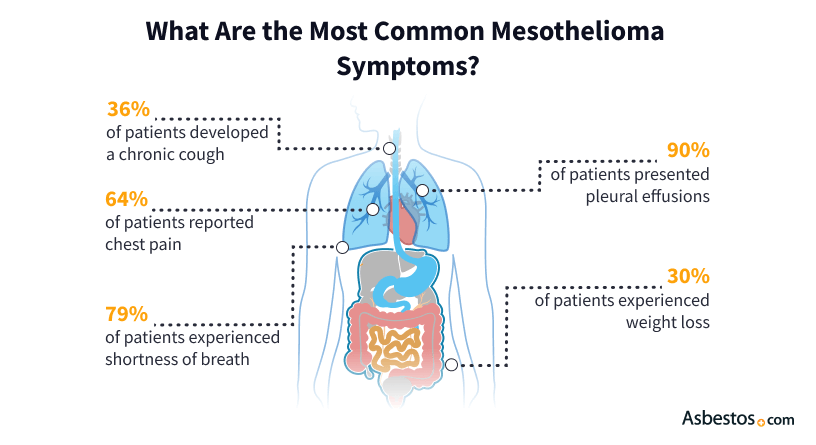
Symptoms of Pleural Mesothelioma
Pleural mesothelioma starts in the protective lining around the outside of the lungs (pleura). Common early-stage signs of pleural mesothelioma include shortness of breath, fatigue, weakness, a dry cough and chest pain.
It’s difficult to diagnose pleural mesothelioma early because symptoms usually don’t appear in stage 1. Most late-stage symptoms involve pain, trouble breathing and difficulty swallowing.
Signs and Symptoms of Pleural Mesothelioma
- Chest pain
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Fatigue or extreme tiredness
- Hoarseness
- Lower back pain
- Lumps in the chest area
- Muscle weakness
- Persistent cough
- Plural effusion
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Swelling of the face and arms
- Unexplained weight loss
Rare signs of pleural mesothelioma are night sweats and clubbed fingers, a condition that causes the tips of the fingers to enlarge. A 2024 study in the journal Cancers found pleural mesothelioma can cause thromboses. These are blood clots that block blood flow in the body. Symptoms will vary depending on the clot’s location.
“Many oncologists, primary care providers and even pulmonologists don’t realize that a pleural effusion or shortness of breath and pain could be mesothelioma because it is so rare,” Dr. Jeffrey Velotta, a cardiothoracic surgeon at Kaiser Permanente Oakland Medical Center, tells us. “If they know what to look for, they can refer patients to mesothelioma specialists.”

Understand your diagnosis, top doctors and ways to afford care.
Get Your Free GuidePeritoneal Mesothelioma Symptoms
Peritoneal mesothelioma is the second most common type of mesothelioma. It forms in the abdominal lining (peritoneum) and often causes abdominal and digestive symptoms.
Abdominal pain is a common peritoneal mesothelioma symptom. A 2023 study in Oncology in Clinical Practice found abdominal distension in 30% to 80% of peritoneal mesothelioma patients. Poor appetite and constipation may go with it. Tumors can also cause small bowel obstruction.
Common Symptoms of Peritoneal Mesothelioma
- Abdominal fluid buildup (ascites)
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal swelling
- Blockage in the small intestine
- Constipation
- Fever and night sweats
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Tiredness
- Unexplained weight loss
Some rare signs of peritoneal mesothelioma include blood clots, hernia, jaundice, low blood sugar and neurological issues like seizures or paralysis. When peritoneal mesothelioma metastasizes or spreads to the liver, intestines and other organs, it can lead to further rare symptoms. Distant metastases are rarer. They occur in only 10% to 50% of stage 4 mesothelioma cases. It can affect distant organs, including the chest and brain.
Isabel De La Camara, a peritoneal mesothelioma survivor, told The Mesothelioma Center that her diagnosis improved her life. “It pushed me to enjoy my life more, to live every moment like it’s your last.” Isabel also said she tells people to enjoy today because tomorrow is not guaranteed for anyone.
Pericardial Mesothelioma Symptoms
Pericardial mesothelioma is a cancer that affects the lining of the heart and is extremely rare. Some signs of the disease include fever, night sweats and weakness. Patients in later stages of the disease may have heart pressure caused by fluid buildup.
Signs and Symptoms of Pericardial Mesothelioma
- Chest pain
- Cough
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
- Fatigue
- Heart murmurs
- Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- Low Blood Pressure
- Shortness of breath when lying down
The rarity of pericardial mesothelioma can make it difficult for doctors to diagnose. The disease accounts for less than 1% of all cases, and only 150 cases exist in medical literature.
“[Pericardial mesothelioma] patients can present with heart failure initially. It’s not unusual to diagnose pericardial mesothelioma as an incidental finding. You’re not suspecting pericardial mesothelioma,” Dr. Wickii Vigneswaran, a thoracic surgeon, told The Mesothelioma Center.
Testicular Mesothelioma Symptoms
Testicular mesothelioma forms in the lining of the testes,known as the tunica vaginalis. The main signs are a lump or swollen testes.
Signs and Symptoms of Testicular Mesothelioma
- Fluid buildup in the scrotum (hydrocele)
- Inguinal hernia
- Lump in the scrotum
- Spermatocele (cyst in the epididymis)
- Swollen testes
- Testicular pain
Other early symptoms of testicular mesothelioma include pain similar to a groin injury. Sometimes, these symptoms are mistaken for an infection of the testes. Testicular mesothelioma is the rarest form of asbestos-related cancer.
| Pleural Mesothelioma % | Peritoneal Mesothelioma % | |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | 70% | 86% |
| Weakness | 59% | 54% |
| Trouble breathing | 63% | 20% |
| Chest pain | 50% | 20% |
| Coughing or wheezing | 51% | 14% |
| Loss of appetite | 44% | 58% |
| Unexplained weight loss | 28% | 42% |
When Should I See a Doctor?
Chest pain, abdominal swelling or a persistent cough are key signs you should see a mesothelioma doctor. This is especially crucial if you have a history of asbestos exposure. Frequent bouts of pneumonia can be signs of an underlying lung disease. Early diagnosis using mesothelioma screening is vital for increased survival rates. Statistics show early detection and intervention improve life expectancy for mesothelioma patients.
Pleural mesothelioma survivor Kim Madril’s cancer journey started with a persistent shooting pain in her left side, which she first thought was a kidney stone. That led to her getting a CAT scan before being diagnosed with mesothelioma. Kim was exposed to asbestos as a teenager in her junior high and high school classrooms. It happened during automotive shop class, art class and ceramics class.
And I had this sharp shooting pain on the left side.
My husband jumped out of bed. He’s like, “what’s wrong?” I said, I think I’m having a kidney stone. And he’s like, alright. Let’s go to the emergency department.
I’m not one to go see doctors, and and I think really I hadn’t been to emergency department in probably 15 years or so. So we ended up there, and they said, “well, you must have passed it because we don’t we don’t see we don’t that we don’t see anything.” I was okay for probably three or four months, and then it came again.
Not to the same degree. And I was kinda like, “Oh, oh, ow, ow!” and it kept happening. And the intervals were coming closer, than than before. They weren’t as spread out.
And so my PCP finally said, “Kim, let’s let’s just, let’s just get a a cat scan. Okay?”
And I said, “oh, okay.” And the CAT scan came back. And he said, there’s something see some sort of nodule, that’s what he called it, a nodule at the base of your left lung. It’s not your kidney. It’s the bottom of your left lung. Which is right about where your kidneys are. And I thought, oh my gosh, I never never thought it would be like a lung thing.
So, I said, oh, okay. And he said, let’s watch it. Because it’s so small right now.
And I said, alright. I’m good with that. But then the pain kept happening. And he said, I’m gonna refer you to a pulmonologist.
And I saw the pulmonologist, And he said, he said, I don’t know Kim. The only thing I can think is you let’s biopsy it. It’s it’s something there. It’s some sort of mask. You keep having pain.
I didn’t have the I didn’t have any problems with shortness of breath. I didn’t have, coughing, excessive coughing.
It was mainly the pain. He said, we just need to biopsy it. So I said, alright. That sounds great.
If you’re experiencing symptoms, see a mesothelioma doctor or your personal doctor. Early treatment is more effective in slowing your cancer and increasing your survival rate.

Discover how mesothelioma doctors personalize treatment plans for you.
Sign up nowManaging Mesothelioma Symptoms
Mesothelioma symptom management can include a combination of palliative therapies to reduce pain and increase comfort with traditional mesothelioma treatments like surgery, chemotherapy and radiation. Immunotherapy can also offer relief but may lead to side effects or challenging recoveries. Supportive therapies further assist patients and families in coping with the emotional toll of the disease.
“Regarding managing symptoms, patients are sometimes challenged with taking pain medication as they worry about being addicted.”
A comprehensive symptom management plan prioritizes overall health by addressing nutrition, exercise and mental well-being. Traditional approaches, such as respiratory, physical and occupational therapy, along with pain medications, are often paired with complementary therapies, like massage, gentle yoga and meditation. Support groups also provide valuable emotional support and coping strategies for patients navigating the challenges of mesothelioma.
- Palliative care helps manage mesothelioma symptoms. It can be given alongside treatment. A 2024 Ottawa Hospital study found only 49% of mesothelioma patients received palliative care.
- Our 2025 survey found similar results with only 50% of respondents receiving palliative care. Talk to your doctor about potential palliative options for symptom management.
“A number of treatments can help ease symptoms and improve quality of life. Discuss all your symptoms with your medical team. “Together, you can find the best treatment for you.”
Common Questions About Mesothelioma Symptoms
- When do mesothelioma symptoms appear?
-
Symptoms of mesothelioma tend to present between 20 and 60 years after asbestos exposure. This delay is known as the latency period. Asbestos exposure, age, and health can affect the latency period.
- Can you have mesothelioma without symptoms?
-
Yes, you may have mesothelioma without any symptoms. Many mesothelioma symptoms are mild and mimic the flu or a stomach virus. Most only appear decades after asbestos exposure. Doctors may misdiagnose this rare cancer as other illnesses. This can delay your mesothelioma diagnosis.
- Can mesothelioma symptoms come on suddenly?
-
Yes, some symptoms may occur suddenly. Some patients have no symptoms until the cancer spreads to other organs. The cancer’s location determines the type and severity of symptoms you may have.







