Pastor, podcaster, writer and pericardial mesothelioma survivor Dr. Berlinda Love tells us after months of chemo, she began immunotherapy and is feeling great. She says with chemo, “I was tired quite a bit, lethargic a lot. I wanted to sleep for 2 or 3 days, but I don’t have those symptoms now.”
Immunotherapy for Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma immunotherapy helps the immune system locate and combat cancer cells. This treatment enhances the body's ability to fight mesothelioma. Immunotherapy for mesothelioma benefits include a longer life, improved quality of life and reduced symptoms.
What Is Immunotherapy for Mesothelioma?
Immunotherapy for mesothelioma is a treatment that uses your own immune system to fight this asbestos-related cancer. Unlike chemotherapy or radiation, which directly attack cancer cells, immunotherapy boosts the body’s natural defenses to recognize and destroy mesothelioma cells.
Mesothelioma immunotherapy has become a standard part of care for many patients in recent years, offering new hope for those with difficult-to-treat tumors. Doctors often use immunotherapy alongside other mesothelioma treatments, such as chemotherapy or surgery, to improve outcomes.
Key Facts About Mesothelioma Immunotherapy
- Combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy often works better than chemotherapy alone, improving response rates and survival for many patients.
- Clinical trials have shown it can extend survival. For example, some patients lived over 1 year longer with immunotherapy than those who received only chemotherapy.
- More patients are accessing immunotherapy every year. In a recent patient survey, 40% of mesothelioma patients said they had tried immunotherapy as part of their treatment plan.
- Immunotherapy is now one of the top treatments for malignant mesothelioma.
“I’ve treated mesothelioma patients who had exhausted older chemotherapy regimens, but improved surgical management and additional immunotherapy options have helped extend their lives in ways we never thought possible just a decade ago,” said Dr. Andrea Wolf, thoracic surgeon and director of the New York Mesothelioma Program at Mount Sinai.
How Does Immunotherapy Work to Treat Mesothelioma?
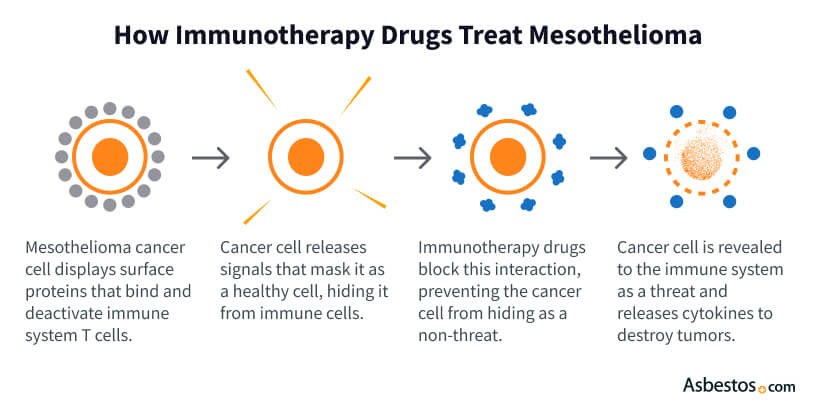
Immunotherapy for mesothelioma can trick the immune system into ignoring cancer cells. This treatment works by kickstarting your immune system’s ability to find and kill cancer cells. It’s similar to how your body fights off infections: Immune cells, like T-cells, seek out invaders (in this case, tumor cells) and destroy them.
Mesothelioma tumors often hide by using special proteins (such as PD-L1) to put the “brakes” on immune cells. Immunotherapy drugs release these brakes and expose the cancer. For example, immune checkpoint inhibitors like Keytruda (pembrolizumab) or Opdivo (nivolumab) block the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway that tumors use to evade detection.
Ipilimumab, or Yervoy, enhances the immune system’s ability to combat mesothelioma by blocking CTLA-4, a protein that aids T-cells in targeting cancer tumors. This treatment can slow tumor growth and reduce tumor size while causing fewer side effects than chemotherapy, which often damages healthy cells.
FDA-Approved Mesothelioma Immunotherapy Drugs
Immunotherapy has become a standard treatment for unresectable pleural mesothelioma thanks to several recent FDA approvals. These immunotherapy drugs use the body’s natural immune response to recognize and fight mesothelioma cancer cells, improving survival outcomes for many patients.
FDA-approved drugs such as Opdivo, Yervoy and Keytruda have significantly changed the standard of care for mesothelioma, particularly for patients who cannot have surgery or whose cancer has spread extensively.
Immunotherapy Drugs Approved to Treat Mesothelioma
- Keytruda (pembrolizumab): Approved in September 2024 for treating unresectable pleural mesothelioma with standard chemotherapy (pemetrexed and platinum), Keytruda shows better tumor response rates and survival than chemotherapy alone.
- Opdivo (nivolumab): FDA-approved with Yervoy (ipilimumab) for first-line treatment of adults with unresectable pleural mesothelioma. Trials like CheckMate 743 demonstrated this combination improves overall survival over traditional chemotherapy.
- Yervoy (ipilimumab): Approved with Opdivo for first-line treatment of unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma, Yervoy targets the CTLA-4 immune checkpoint, enhancing the immune system’s ability to destroy cancer cells.
These immunotherapy treatments represent the current gold standard for mesothelioma patients who cannot undergo surgery. While Keytruda combined with chemotherapy offers strong results for many patients, the Opdivo and Yervoy combination has shown particular effectiveness for non-epithelioid mesothelioma.
Patients with unresectable pleural mesothelioma now have these FDA-approved immunotherapy options as part of their frontline treatment plan, providing new hope and extended survival compared to previous therapies.

Discover how mesothelioma doctors personalize treatment plans for you.
Sign up nowExperimental Mesothelioma Immunotherapies & Clinical Trials
Research on immunotherapy for mesothelioma is advancing, with promising therapies in clinical trials, including CAR T-cell therapy, cancer vaccines and oncolytic viruses. In May 2024, the FDA fast-tracked Keytruda’s review with chemotherapy for pleural mesothelioma.
Trials like DREAM3R and CheckMate 743 compare immunotherapy to chemotherapy to identify the most effective treatment. Participation in clinical trials allows patients to access innovative therapies early. Researchers want to make these methods available to all to help mesothelioma patients live longer and better lives.
CAR T-Cell and Protein Therapies
CAR T-cell therapy is a type of treatment in which doctors take immune cells (T-cells) from the patient’s blood, modify them in a lab to better fight cancer, and then return these powerful cells to the patient’s body. This approach helps the immune system more effectively target and attack mesothelioma tumors.
Several mesothelioma clinical trials using CAR T-cell therapies are recruiting participants in the U.S. One major trial at the National Cancer Institute combines mesothelin-targeted CAR T-cells with pembrolizumab to enhance treatment. These trials improve CAR T-cell therapy for safer, stronger and longer-lasting responses against mesothelioma tumors.
Mesothelioma Cancer Vaccines
Cancer vaccines train the body’s immune system to recognize and attack mesothelioma cells. Unlike regular vaccines that prevent diseases like the flu, cancer vaccines help fight cancer that is already present. These vaccines expose the immune system to proteins unique to mesothelioma, teaching it to target and destroy the cancer cells more effectively.
Several mesothelioma vaccine trials are ongoing in the U.S. The WT1 vaccine (galinpepimut-S) targets a protein in mesothelioma cells and shows promise in improving survival. Another trial studies CRS-207, using modified bacteria to stimulate an immune response against mesothelioma. These trials offer hope that vaccines may be crucial for future treatments.
Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are synthetic proteins that act like guided missiles in immunotherapy. They locate and attach themselves to specific targets on cancer cells, helping the immune system recognize and destroy these harmful cells. Monoclonal antibodies that work this way are a type of immunotherapy for mesothelioma.
In mesothelioma treatment, monoclonal antibodies like amatuximab target mesothelin, a protein commonly found on mesothelioma cells. Another antibody, tremelimumab, targets CTLA-4 to enhance the immune response. Currently, multiple trials involving monoclonal antibodies for mesothelioma are active and recruiting patients.
Virotherapy
Virotherapy, or oncolytic virus therapy, is an immunotherapy that uses engineered viruses to target and kill mesothelioma cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. These viruses infect mesothelioma cells, causing them to burst and release substances that activate the immune response against cancer.
Researchers are exploring several viruses as immunotherapy for mesothelioma, including adenoviruses, measles, herpesviruses and reoviruses. Though virotherapy is still experimental, early results have shown promising potential for future mesothelioma treatments by shrinking tumors and boosting the immune response in mesothelioma.
Benefits of Immunotherapy for Mesothelioma
Immunotherapy offers fewer side effects, targeted action and several other key benefits for mesothelioma patients that set it apart from conventional treatments. JAMA Network Open in 2024 published a study on the success of immunotherapy and noted that while results can vary, many patients experience longer survival and a better quality of life with immunotherapy.
Mesothelioma immunotherapy greatly improves mesothelioma outcomes, providing longer survival and better cancer control. Many patients live 2 to 5 years beyond their prognosis. Compared to chemotherapy, immunotherapy for mesothelioma typically has fewer side effects, enabling patients to maintain their daily activities.
Mesothelioma Immunotherapy Success Rates
- Mesothelioma patients who underwent immunotherapy have a 41% 2-year survival rate, compared to 27% with chemotherapy.
- Keytruda offers 18 months of survival for recurrent cases.
- Opdivo and Yervoy provide an average survival of 18.1 months.
These therapies specifically target cancer cells, protecting healthy tissues. Treatment is personalized based on each patient’s cancer markers, increasing the chances of success. Plus, immunotherapy complements chemotherapy or surgery to improve patient outcomes.
The most significant benefit of immunotherapy for mesothelioma is hope for a cure. Mesothelioma patients and families now have more options to try, even after standard treatments. Seeing tumors shrink from immunotherapy or hearing that a therapy keeps the cancer stable can be highly encouraging.
Who Is a Candidate for Mesothelioma Immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy has become an important treatment option for many mesothelioma patients, particularly those with advanced or unresectable mesothelioma. However, eligibility can depend on several factors, including previous treatments, overall health and specific tumor characteristics.
Dr. Catherine Perrault, a medical officer with The Mesothelioma Center’s Medical Outreach Program, emphasized in her webinar that while certain mesothelioma cell types may respond differently to immunotherapy, having a specific type does not necessarily disqualify a patient from receiving immunotherapy.
Factors Influencing Candidacy for Mesothelioma Immunotherapy
- Cell type: Patients with nonepithelioid mesothelioma (sarcomatoid or biphasic) often respond better to immunotherapy than chemotherapy.
- Overall health and performance status: Doctors use the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group status to assess whether a patient is healthy enough for immunotherapy.
- PD-L1 biomarker status: High PD-L1 levels may predict better response, but patients with low or negative PD-L1 can still benefit from immunotherapy.
- Previous treatment response: Patients whose mesothelioma progressed or returned after chemotherapy may qualify for immunotherapy as a second-line treatment.
- Stage and operability: Patients with advanced, metastatic, or unresectable mesothelioma are typically prime candidates for immunotherapy.
Each mesothelioma patient’s case is unique, and specialists evaluate these factors individually to decide if immunotherapy is the best choice. Even patients who have not responded well to earlier treatments can benefit from immunotherapy.
Mesothelioma clinical trials may also provide immunotherapy options when standard therapies aren’t suitable or available, offering new hope for improved quality of life and extended survival.

Discover new treatments with immunotherapy clinical trials near you.
Sign Up NowMesothelioma Immunotherapy Side Effects
Immunotherapy can significantly improve mesothelioma outcomes, but patients can also experience side effects. These side effects often result from the immune system becoming overly active, causing symptoms similar to the flu or mild autoimmune reactions.
For mesothelioma patients, specific side effects, such as coughing and shortness of breath, can be challenging for doctors to interpret because these symptoms are also common signs of pleural mesothelioma. This overlap makes it essential for patients and doctors to communicate clearly about any new or worsening symptoms during treatment.
Common Immunotherapy Side Effects
Because mesothelioma often affects lung function, respiratory side effects such as coughing or shortness of breath require special attention to distinguish between disease progression and treatment response.
Patients should promptly inform their doctors of these symptoms, so their medical team can accurately manage treatment and symptom relief. Regular check-ups and good communication with healthcare providers help mesothelioma patients maintain comfort and quality of life during immunotherapy.
Serious Side Effects
Although rare, serious immune-related adverse events can occur in mesothelioma patients when their immune system becomes overly aggressive, attacking healthy tissues instead of cancer cells. These adverse events can cause significant inflammation in critical organs, and doctors must manage them swiftly to avoid permanent damage or interruption of treatment.
Severe Immunotherapy Side Effects
- Colitis: Severe inflammation of the colon causing persistent diarrhea, abdominal pain or blood in the stools.
- Endocrine gland disorders: Problems with glands causing hormonal imbalance, fatigue, mood swings or rapid heartbeat.
- Hepatitis: Liver inflammation causing yellow skin (jaundice), dark urine or abdominal pain.
- Kidney inflammation (nephritis): Kidney inflammation leads to swelling, decreased urine output or lower back pain.
- Pneumonitis: Lung inflammation causing chest pain, severe coughing and breathing difficulty.
Doctors usually treat severe reactions with steroids or other medicines that weaken the immune system. Specialists monitor patients through regular blood tests and check-ups to find side effects early.
If serious side effects happen, your mesothelioma doctor may suggest stopping or pausing immunotherapy to keep you safe. Patients should quickly tell their doctors about any new or worse symptoms and talk about how to manage treatment safety and side effects.
- Some types of immunotherapy for mesothelioma have already been approved for advanced, malignant and inoperable cases, according to a 2025 study published in the medical journal Cancers. Clinical trials are exploring more immunotherapy and chemotherapy combinations as first-line treatments.
- Our exclusive 2025 survey found 22% of mesothelioma patients used immunotherapy as part of their personalized treatment plan.
“This has really helped improve treatment outcomes in mesothelioma, whether in unresectable or even respectable mesothelioma; thus, more research in immunotherapy is crucial to improving outcomes.”
Common Questions About Immunotherapy for Mesothelioma
- Does insurance cover immunotherapy?
-
Yes, insurance usually covers immunotherapy for mesothelioma if the treatments are FDA-approved. Medicare, private insurance and VA health care typically pay for drugs like Keytruda, Opdivo and Yervoy, which lowers out-of-pocket costs. Although immunotherapy can be expensive, as much as $100,000 or more annually for some checkpoint inhibitors, financial aid programs and clinical trials can help pay for it for those who qualify.
- How long do patients stay on immunotherapy?
-
Mesothelioma patients usually stay on immunotherapy until their cancer worsens or side effects become hard to handle, often lasting from a few months to about two years. In clinical trials, immunotherapy is often given for two years. However, how long treatment lasts can differ based on each patient’s response and health situation.
- Is immunotherapy equally effective for men and women?
-
Studies show that both men and women benefit from immunotherapy for mesothelioma, but the response rates may be a bit different. Men may have a slightly better survival rate, but both genders can benefit from these treatments. Doctors recommend all eligible mesothelioma patients to consider immunotherapy options.
- Is immunotherapy better than chemotherapy?
-
Immunotherapy is not always better than chemotherapy, but it usually has fewer side effects and helps patients live longer. It works well for people with nonepithelioid mesothelioma, who often do not respond well to chemotherapy. A mix of immunotherapy and chemotherapy often gives the best results, combining the benefits of both types of treatment.
- How can I access mesothelioma immunotherapy treatment?
-
To begin immunotherapy, talk to a mesothelioma specialist or oncologist to see if FDA-approved or experimental options are right for you. Our Patient Advocates can help you find treatment centers, set up appointments, and handle insurance or VA claims. If FDA-approved therapies aren’t available, they can also help you look for clinical trials to access new treatments early.





